SDG4 - QUALITY EDUCATION
Courses tagged with "SDG4 - QUALITY EDUCATION"
GRPH405 unit–along with GRPH406- comprise the final Graduation Project in one of the four major fields of the Graphics & Media Arts Department in response to a self-initiated design agenda/brief. Students will finally exploit all their expertise and previous experiences acquired throughout their unit of study to accomplish their final Graphics and Media Arts project.
In this unit students will execute one final research project representing their knowledge, skills and cultural awareness gained in the previous years of study that is closely related to the SDGs. The student will choose one of the four major fields in the Graphic and Media Art department and will focus all his/her tools to accomplish the desired outcome. Students are expected to hand in a final dissertation reflecting the entire process they went through, the background, the context, the literature review and analysis/ critique.
GRPH405 unit will focus on collecting information, literature, analysis in the form of researches, reports, presentations, peer to peer assessment, critiques, and one on one tutorial as well as laying the solid base for the practical visual outcome throughout sketches and technical experimentation. A final dissertation is presented by the end of this unit.
- Teacher: Dr.Sara Ahmed Sayed Ali
- Teacher: Dr.Tamer Assem Ali
- Teacher: Ahmed Ayman Abd Elaleem Nagy
- Teacher: Mariam Ayman Fathy Elnabawy
- Teacher: Basma Barakat Abu Bakr Salih
- Teacher: Alaa El-Gammal
- Teacher: Shaimaa Elsherbeny
- Teacher: Eman Gibrel Ahmed Mohamed
- Teacher: Jana Khaled Gamal Eldin Ellaithy
- Teacher: Marwa Mohamed Abd Elaziz Sherif
- Teacher: Menna Mohamed Zakaria
- Teacher: Dr.Eman Nabil Saad Ibrahem
- Teacher: Hisham Nagy Abdelmonem
- Teacher: Amira Sabry Ahmed
- Teacher: Nagwa Yehia Mohamed El adwy
- Teacher: Rania ezzat amin mahmoud
- Teacher: Dr.Dina gamal abboud
- Teacher: Reem Abdelhakeem Abdelqader Mahmoud
- Teacher: Walid Anwar Mohamed Khairy Alraffey
- Teacher: Mariam Hatem Hagar
The aim of the regulatory & ethical aspects
of biotechnology course is to enable students the ability to debate opinions
effectively and base their opinions efficiently in bioethics. The course gives
information about the essential concepts in applying ethics in new sciences
such as gene patenting, transhumanism, stem cell technology, usage of
Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs) and their dilemmas and brain death.
Moreover, the course provides a full understanding of the biohazards
accompanying wrong use of biotechnological science
- Teacher: Yasmin Abdel Latif Mahmoud
- Teacher: Shaza Ahmed Abd Allah Habib
- Teacher: Samer El Sayed Mohamed El Sayed Ismail
- Teacher: Shaadi Elswaifi
- Teacher: Shaadi Elswaifi
- Teacher: Salwa Farouk Sabet
- Teacher: Khaled Mohamed Ahmed Emam Sharafeldin
- Teacher: Amr Mohamed Mahmoud Ageez
- Teacher: Ahmed Mohamed Refaat Elsayed
- Teacher: Riham Mohsen Mohamed
- Teacher: Ali Mohsen Youssef Ahmed
- Teacher: Amgad Mostafa Mohamed El Said
- Teacher: Haidan Mostafa Salem
- Teacher: Mohamed Salah El-Din Hodhod
- Teacher: Hossam Taha Mohamed Abd El Moneam
- This course is a universal repository for all courses at MSA with a large number of potential TEL tools.
- Coordinators of all courses at MSA faculties are encouraged to import any resource(s) they like from this course to their respective courses.
- Teacher: Islam ElShaarawy
- Teacher: Ali Hamed Bastawesy
- Teacher: computer science MSA

Functions-Properties of Functions – Composite Functions-Limits – Computational Techniques of Limits. Continuty – Limits and Continuty of Ttrigonometric Functions- The Derivative – Techniques of Differentiation – Derivative of Trignometric Functions – The Chain Rule – Implicit and parametric Differentiation-Inverse Functions – Logarithmic and Exponential Functions – Inverse Trignometric Functions – Hyprbolic Functions – Inverse Hyperbolic Functions- L'Hopital Rule – Indeterminate Forms - Taylor and Maclurin series -Functions of Two or More Variables – Partial Derivatives – Chain Rules.
- Teacher: Dr.Ghada Abdelhady
- Teacher: Prof.Magd Elias Kahil
- Teacher: Diaa Hafez
- Teacher: Marine Maher Mauric Guirguis
- Teacher: Maysa Mahmoud Fathy Omar
- Teacher: Dr.Nabila Nowaira
- Teacher: Prof.Dr.Hafez Radi
- Teacher: Prof.Nahed Sobhi abd elnour
- Teacher: Mona afifi

- Define types of data, simple model of computer, data storage, data processing, integrated circuits (ICs), and registers.
- Recognize number systems and coding schemas.
- Identify the functions of OS, basics of programming languages, and computer software categories.
- Apply computer skills on mini-projects serving different engineering departments.
- Explain the types of computer networks and data communication.
- Organize the information security, Malicious Software, and solutions.
- Have a view on the concepts and the future of AI & IoT.

- Teacher: Dr.Ghada Abdelhady
- Teacher: Diaa Hafez
- Teacher: Alaa Hashem Mohamed Abd Elrahman
- Teacher: Maysa Mahmoud Fathy Omar
- Teacher: Yasmina Mohamed Taha
- Teacher: Dr.Nabila Nowaira
- Teacher: Prof.Dr.Hafez Radi
- Teacher: Mina Samir Shenouda Abdelnour
- Teacher: Prof.Nahed Sobhi abd elnour
- Teacher: Mona afifi
The Mechanics 1 (Statics) module is designed to cover:
- Units and Forces
- Statics of Particles: Plane
- Statics of Particles: Space
- Statics of Rigid Bodies: Vector Product
- Statics of Rigid Bodies: Moments, Moment – Couple and Wrench
- 2-D Equilibrium Structure
- 3-D Equilibrium Structure
- 2-D Centroids and Center of Gravity, 3-D Centroids and Center of Gravity
- 2-D Moment of Inertia, 3-D Moment of Inertia, Real Case Studies.
- Teacher: Hossam Abd Elghaffar
- Teacher: Adham Ahmed Elsayed Abdelmagid
- Teacher: Fatma Elzahraa Basyony Ismail
- Teacher: Diaa Hafez
- Teacher: Maha Ibrahim
- Teacher: Maysa Mahmoud Fathy Omar
- Teacher: Dr.Nabila Nowaira
- Teacher: Prof.Dr.Hafez Radi
- Teacher: Prof.Nahed Sobhi abd elnour
- Teacher: Mona afifi
*Recognize the importance of the theory of
differential equations and understand the relation between differential
equations and various fields of sciences.
* Formulate the essential facts, concepts, principles and theories related to
the theory of differential equations.
* Use analytic methods for solving ordinary differentia equations which appear in engineering applications.
* Employ recent communication and information technologies, models and tools effectively in different numerical methods..
- Teacher: Dr.Ghada Abdelhady
- Teacher: Diaa Hafez
- Teacher: Youssef Hany Moustafa El-Habashy
- Teacher: Alaa Hashem Mohamed Abd Elrahman
- Teacher: Maysa Mahmoud Fathy Omar
- Teacher: Dr.Noha Moustafa
- Teacher: Dr.Nabila Nowaira
- Teacher: Prof.Dr.Hafez Radi
- Teacher: Prof.Nahed Sobhi abd elnour
- Teacher: Mona afifi
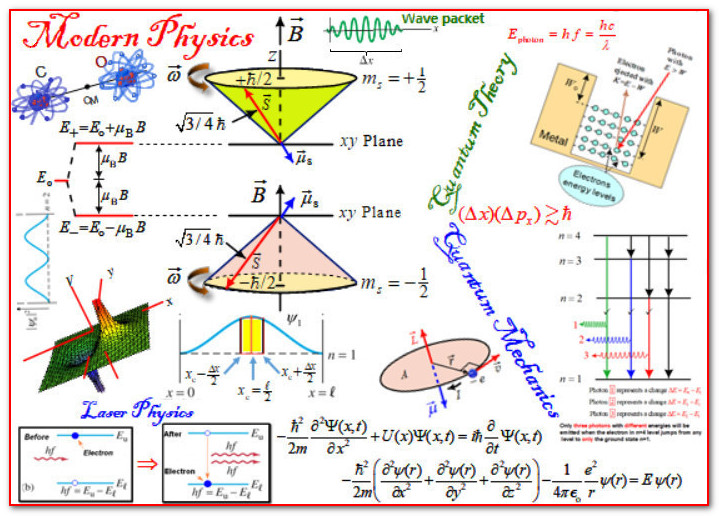
The Modern Physics module is designed to cover in depth:
· The special theory of relativity
· Blackbody radiation and the photoelectric effect
· The Compton Effect, wave properties of a particles, and the uncertainty principle
· Bohr’s theory of atom and atomic spectra
· Quantum mechanical model of the Hydrogen atom
· The electron Spin, the Zeeman Effect, and Laser Physics
- Teacher: Rawan Elshahawi Elsaeid Elsayed
- Teacher: Diaa Hafez
- Teacher: Dr.Samer Ibrahim Mohamed
- Teacher: Maysa Mahmoud Fathy Omar
- Teacher: Dr.Nabila Nowaira
- Teacher: Prof.Dr.Hafez Radi
- Teacher: Prof.Nahed Sobhi abd elnour
- Teacher: Mona afifi

- Teacher: Diaa Hafez
- Teacher: Nayera Hassan Ali Ibrahim
- Teacher: Ahmed M. D. E. Hassanein
- Teacher: Maysa Mahmoud Fathy Omar
- Teacher: Abdelrahman Mohamed Ali Hassan El-Akhdar
- Teacher: Dr.Nabila Nowaira
- Teacher: Farah Raad Kareem
- Teacher: Prof.Dr.Hafez Radi
- Teacher: Prof.Nahed Sobhi abd elnour
- Teacher: Nada Yasser Ahmed Salama
- Teacher: Mona afifi

This module is designed to enable students to cope up with new advances in research in electronics. It includes a review of Electronics available today and the new trends in Electronics research.
- Teacher: Mohamed Gamal Shafeek
- Teacher: Diaa Hafez
- Teacher: Ahmed M. D. E. Hassanein
- Teacher: Maysa Mahmoud Fathy Omar
- Teacher: Dr.Nabila Nowaira
- Teacher: Farah Raad Kareem
- Teacher: Prof.Dr.Hafez Radi
- Teacher: Prof.Nahed Sobhi abd elnour
- Teacher: Mona afifi

This module is designed to enable students to focus on the design and analysis of the active circuits, active filters, multiple feedback operational amplifiers, and multiple feedback filters. It also provides considerable understanding and confidence in Engineering Electronics and develops the intellectual and practical skills necessary for Electronics Engineering area.
- Teacher: Ahmed Gamal Ahmed Mohamed Elsherif
- Teacher: Diaa Hafez
- Teacher: Ahmed M. D. E. Hassanein
- Teacher: Maysa Mahmoud Fathy Omar
- Teacher: Dr.Maher Mohamed El-Tayeb
- Teacher: Nesma Nour
- Teacher: Dr.Nabila Nowaira
- Teacher: Farah Raad Kareem
- Teacher: Prof.Dr.Hafez Radi
- Teacher: Prof.Nahed Sobhi abd elnour
- Teacher: Mona afifi

This module is designed to enable students to cope up with new advances in research in Communication. It includes a review of Communications available today and advances in Communications research.
- Teacher: Nourhan Ahmed Yehia Saad Mahmoud Hassan
- Teacher: Ahmed Fawzy Daw / Dr
- Teacher: Diaa Hafez
- Teacher: Ahmed Hatem
- Teacher: Ahmed I. Ahmed
- Teacher: Dr.Samer Ibrahim Mohamed
- Teacher: Ahmed M. D. E. Hassanein
- Teacher: Maysa Mahmoud Fathy Omar
- Teacher: Shaymaa Mohamed Tayser El-Sayed
- Teacher: Dr.Nabila Nowaira
- Teacher: Farah Raad Kareem
- Teacher: Prof.Dr.Hafez Radi
- Teacher: Shahenaz Shokry
- Teacher: Prof.Nahed Sobhi abd elnour
- Teacher: Mona afifi

This module is designed to provide students with the necessary fundamentals of robotics including kinematics, dynamics, motion planning, computer vision, and control.
- Teacher: Diaa Hafez
- Teacher: Ahmed M. D. E. Hassanein
- Teacher: Dina Magdy Abd Elkader Elsayed
- Teacher: Ahmed Mahmoud Abdelrahman Mohamed Alenany
- Teacher: Maysa Mahmoud Fathy Omar
- Teacher: Mai Mohamed Mahmoud Mohamed
- Teacher: Youmna Muhammad Abd Elmoneim
- Teacher: Dr.Nabila Nowaira
- Teacher: Farah Raad Kareem
- Teacher: Prof.Dr.Hafez Radi
- Teacher: Prof.Nahed Sobhi abd elnour
- Teacher: Mona afifi

This module is designed to provide students with an in-depth overview of the Radar systems and covers the growth of Radar Technology and applications. Basics Radar Equation, Radar theory of operation, Radar types, Radar Operating modes and different Radar modules are also introduced.
- Teacher: Ibrahim Ahmed Haroun
- Teacher: Hagar Ahmed Mahmoud Ahmed Morad
- Teacher: Mohamed Alamir Faisal
- Teacher: Amira El-Tokhy
- Teacher: Ahmed Fawzy Daw / Dr
- Teacher: Alshaimaa Gamal Ramadan
- Teacher: Diaa Hafez
- Teacher: Ahmed M. D. E. Hassanein
- Teacher: Maysa Mahmoud Fathy Omar
- Teacher: Abdelrahman Mohamed Ali Hassan El-Akhdar
- Teacher: Dr.Nabila Nowaira
- Teacher: Farah Raad Kareem
- Teacher: Prof.Dr.Hafez Radi
- Teacher: Samar Sameh Mohamed Farouk
- Teacher: Mohamed Sayed Zaky El Atrash
- Teacher: Prof.Nahed Sobhi abd elnour
- Teacher: Mona afifi

This module is designed to provide students with the necessary knowledge about communication, transmission and systems, and how all relate to what we do everyday. The students will examine source, encoder (transmitter), channel, and receiver functions in communication transmissions of all types. Emphasis will be placed on principles of line(wired)and air (wireless) communication, a study of various systems, and future developments in communication transmission systems.
- Teacher: Muhammad Abd El-Hady Ghonaim
- Teacher: Fady Erian Estafanous
- Teacher: Ahmed Gamal Ahmed Mohamed Elsherif
- Teacher: Diaa Hafez
- Teacher: Ahmed M. D. E. Hassanein
- Teacher: Maysa Mahmoud Fathy Omar
- Teacher: Dr.Hazem Mohamed Fawzy Zakaria Eissa
- Teacher: Ahmed Mohamed Mohamed Abdelrazek
- Teacher: Dr.Nabila Nowaira
- Teacher: Farah Raad Kareem
- Teacher: Prof.Dr.Hafez Radi
- Teacher: Prof.Nahed Sobhi abd elnour
- Teacher: Mona afifi

This module is designed to provide students with the necessary practical skills to design and build electronic projects, to improve his/her practical background in control systems, to use engineering software as MATLAB and SIMULINK, and to strengthen his/her practical skills in different electronics areas that might have been neglected and to improve his/her technical writing style. Lectures are designed according to the need of the projects.
- Teacher: Diaa Hafez
- Teacher: Ahmed M. D. E. Hassanein
- Teacher: Maysa Mahmoud Fathy Omar
- Teacher: Dr.Nabila Nowaira
- Teacher: Farah Raad Kareem
- Teacher: Prof.Dr.Hafez Radi
- Teacher: Prof.Nahed Sobhi abd elnour
- Teacher: Mona afifi

This module is designed to provide students with the necessary knowledge about instrumentations and controllers used in industrial process control. It introduces process characteristics, modeling of simple systems, controller tuning, and designing closed feedback control.
- Teacher: Ahmed Gamal Ahmed Mohamed Elsherif
- Teacher: Diaa Hafez
- Teacher: Nayera Hassan Ali Ibrahim
- Teacher: Ahmed I. Ahmed
- Teacher: Ahmed M. D. E. Hassanein
- Teacher: Maysa Mahmoud Fathy Omar
- Teacher: Dr.Nabila Nowaira
- Teacher: Farah Raad Kareem
- Teacher: Prof.Dr.Hafez Radi
- Teacher: Prof.Nahed Sobhi abd elnour
- Teacher: Mona afifi

This module is designed to provide students with the necessary knowledge about Direct sequence Code division multiple access (DS-CDMA), Multi carrier techniques: Orthogonal Frequency division multiple access (OFDM) and Multicarrier CDMA (MC-CDMA), Miscellaneous Current and New Technologies: Wide band CDMA(W-CDMA), Ultra Wideband (UWB) communications, Wireless Fidelity (Wi-Fi), and Radio Frequency Identification (RFID).
- Teacher: Abderahman Adam Ahmed Adam
- Teacher: Mohamed Gamal Shafeek
- Teacher: Diaa Hafez
- Teacher: Ahmed Hatem
- Teacher: Ahmed M. D. E. Hassanein
- Teacher: Maysa Mahmoud Fathy Omar
- Teacher: Abdelrahman Mohamed Ali Hassan El-Akhdar
- Teacher: Dr.Nabila Nowaira
- Teacher: Farah Raad Kareem
- Teacher: Prof.Dr.Hafez Radi
- Teacher: Mohamed Sayed Zaky El Atrash
- Teacher: Prof.Nahed Sobhi abd elnour
- Teacher: Mona afifi

This module is designed to introduce students to analytical tools and methods that are currently used in digital image processing. It introduces human visual system and image model. Digital image processing tools are used in the laboratory for image restoration, enhancement and compression.
- Teacher: Nourhan Ahmed Yehia Saad Mahmoud Hassan
- Teacher: Mohamed Gamal Shafeek
- Teacher: Diaa Hafez
- Teacher: Omnia Hamdy Abdelrahman Nematallah
- Teacher: Ahmed Hatem
- Teacher: Ahmed M. D. E. Hassanein
- Teacher: Maysa Mahmoud Fathy Omar
- Teacher: Somaia Mohamed
- Teacher: Dr.Hazem Mohamed Fawzy Zakaria Eissa
- Teacher: Dr.Nabila Nowaira
- Teacher: Farah Raad Kareem
- Teacher: Prof.Dr.Hafez Radi
- Teacher: Prof.Nahed Sobhi abd elnour
- Teacher: Nourhane Tarek Ibrahim Hassan
- Teacher: Mona afifi

This module is designed to introduce students to wireless personal communications, one of the fastest growing fields in the engineering world. Technical concepts are at core of design, implementation, research, and history of wireless communication systems are presented followed by current and evolving wireless communication systems and standards.
- Teacher: Hissam Abdel Aziz Ibrahim Selmy
- Teacher: Abderahman Adam Ahmed Adam
- Teacher: Ahmad Amr Abdelkader Ahmad ElMoslimany
- Teacher: Veronia Ayman Adly
- Teacher: Diaa Hafez
- Teacher: Mohamed Hassan
- Teacher: Dr.Emadeldin Helmy
- Teacher: Ahmed M. D. E. Hassanein
- Teacher: Maysa Mahmoud Fathy Omar
- Teacher: Mona Mamdouh Sayed
- Teacher: Abdelrahman Mohamed Ali Hassan El-Akhdar
- Teacher: Shaymaa Mohamed Tayser El-Sayed
- Teacher: Dr.Nabila Nowaira
- Teacher: Farah Raad Kareem
- Teacher: Prof.Dr.Hafez Radi
- Teacher: Neven Saleh Khalil Saleh
- Teacher: Dr.Deena Salem
- Teacher: Prof.Nahed Sobhi abd elnour
- Teacher: Mona afifi

This course is designed to enable students to evaluate the materials of optoelectronics, Light propagation in media, Light propagation in waveguides, Electronic properties of semiconductors, Transport and optical properties of semiconductors, Light detection and imaging, The light enitting diode, The laser diode, and optical fibers.
- Teacher: Diaa Hafez
- Teacher: Dr.Samer Ibrahim Mohamed
- Teacher: Ahmed M. D. E. Hassanein
- Teacher: Maysa Mahmoud Fathy Omar
- Teacher: Dr.Hazem Mohamed Fawzy Zakaria Eissa
- Teacher: Shahenda Mohamed Shokry
- Teacher: Dr.Manal Mourad
- Teacher: Nesma Nour
- Teacher: Dr.Nabila Nowaira
- Teacher: Farah Raad Kareem
- Teacher: Prof.Dr.Hafez Radi
- Teacher: Mohamed Sayed Zaky El Atrash
- Teacher: Shahenaz Shokry
- Teacher: Prof.Nahed Sobhi abd elnour
- Teacher: Mona afifi
- Teacher: sameh mohamed
- Teacher: Dr.walied mohammed nabil

- Teacher: Kamel Abd El Fattah Mohamed
- Teacher: Fady Erian Estafanous
- Teacher: Diaa Hafez
- Teacher: Ahmed M. D. E. Hassanein
- Teacher: Maysa Mahmoud Fathy Omar
- Teacher: Dr.Nabila Nowaira
- Teacher: Farah Raad Kareem
- Teacher: Prof.Dr.Hafez Radi
- Teacher: Bishoy Raouf Saleeb
- Teacher: Yomna Sameer Abd Rabbo Elkho
- Teacher: Mohamed Sayed Zaky El Atrash
- Teacher: Prof.Nahed Sobhi abd elnour
- Teacher: Shrouk Tarek Mohamed
- Teacher: Nada Yasser Ahmed Salama
- Teacher: Mona afifi
- Teacher: sameh mohamed

This
module is designed to enable students to analyze concepts in the data
communication systems including protocols and standards, network configuration
and topologies, analog and digital signals, encoding and modulation techniques,
interfaces and modems, guided and unguided transmission media, multiplexing,
and error detection and correction methods.
- Teacher: Muhammad Abd El-Hady Ghonaim
- Teacher: Dr.Ghada Farouk
- Teacher: Ahmed Gamal Ahmed Mohamed Elsherif
- Teacher: Diaa Hafez
- Teacher: Mohamed Hassan
- Teacher: Sherif Kamel Hussein
- Teacher: Ahmed M. D. E. Hassanein
- Teacher: Maysa Mahmoud Fathy Omar
- Teacher: Dr.Hazem Mohamed Fawzy Zakaria Eissa
- Teacher: Dr.Nabila Nowaira
- Teacher: Farah Raad Kareem
- Teacher: Prof.Dr.Hafez Radi
- Teacher: Bishoy Raouf Saleeb
- Teacher: Mohamed Sayed Zaky El Atrash
- Teacher: Prof.Nahed Sobhi abd elnour
- Teacher: Nourhane Tarek Ibrahim Hassan
- Teacher: Mona afifi
- Teacher: Dr.walied mohammed nabil

This course is designed to enable students to focus on the analysis of the Oscillators, linear and non-linear wave shaping, sweep generator, and voltage regulators.
- Teacher: Ahmed Fawzy Daw / Dr
- Teacher: Diaa Hafez
- Teacher: Ahmed M. D. E. Hassanein
- Teacher: Maysa Mahmoud Fathy Omar
- Teacher: Dr.Nabila Nowaira
- Teacher: Farah Raad Kareem
- Teacher: Prof.Dr.Hafez Radi
- Teacher: Prof.Nahed Sobhi abd elnour
- Teacher: Mona afifi