SDG16 - PEACE,JUSTICE AND STRONG INSTITUTIONS
Courses tagged with "SDG16 - PEACE,JUSTICE AND STRONG INSTITUTIONS"
Clinical Operative Dentistry 3 (RES531a)
|
Discourse Analysis (LN301)
Discourse Analysis- frequently known as “language use above the level of the sentence” provides students with the opportunity to study the meaningful production and interpretation of texts and talk. students get introduced to the field of Discourse Analysis in order to unpack texts for generating meaning and bind it with their study of society and culture. They will gain an advanced understanding of the concept of ‘context’ and its relevance in the process of the production of meaning. The course provides students with frameworks and tools to examine and critique texts and instances of language use that is much relevant to socio-economic and socio-cultural issues such as gender, social power and minorities, environment, health and pandemics
Comparative Literature II - LIT302
Animal studies is among the budding fields that is attracting a lot of attention over the past two decades. This is partially due to the cultural and conceptual shifts in the figuration of animals from mere objects, serving the humans, to subjects in their own rights. Admittedly, such shifts are triggered by our growing awareness of environmental and animal rights questions in what may be deemed a post-human age.
PHIL301 - Philosophical Thinking (Phil301/PHIL301o)
This course provides students with an understanding of western philosophic concepts that formed the foundations of modern civilization. It also addresses major issues that relate to the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) such as establishing justice & peace, reducing inequalities and building strong political institutions. As such, the course complements knowledge acquired by MSA students of English Studies in the fields of culture, enhances their skills in the analysis of socio-cultural phenomena in literature, develops their Problem-solving skills, communication skills, persuasive powers and writing skills. In addition, the course helps students develop sound methods of research and analysis as well as tools to evaluate and criticize different trends of thought.
Graduation Project II (ECO420II)
This unit aims to enhance the students’ knowledge and skills needed to conduct a research paper of substantial depth and length under the supervision of a faculty member, whether it is theoretical based on literature review and analysis, or empirical based on econometric, statistical or mathematical analysis.
Topics selected by students for their graduation projects are closely linked to sustainable development goals, especially SDG8 related to decent work and economic growth, as they create models where they try to determine the main catalysts for growth in certain countries or regions. Students also choose topics related to reducing poverty (SDG1) or inequality (SDG10), quality education (SDG4) gender equality (SDG5) and many other SDGs.Graduation Project I (ECO420I)
This unit aims to enhance the students’ knowledge and skills needed to conduct a research paper of substantial depth and length under the supervision of a faculty member, whether it is theoretical based on literature review and analysis, or empirical based on econometric, statistical or mathematical analysis.
Topics selected by students for their graduation projects are closely linked to sustainable development goals, especially SDG8 related to decent work and economic growth, as they create models where they try to determine the main catalysts for growth in certain countries or regions. Students also choose topics related to reducing poverty (SDG1) or inequality (SDG10), quality education (SDG4) gender equality (SDG5) and many other SDGs.
Macroeconomic Theory I
Macroeconomics is concerned with the understanding of aggregate phenomena such as economic growth, business cycles, unemployment, inflation, and international trade among others. ... These topics are of particular relevance for the development and evaluation of economic policy.
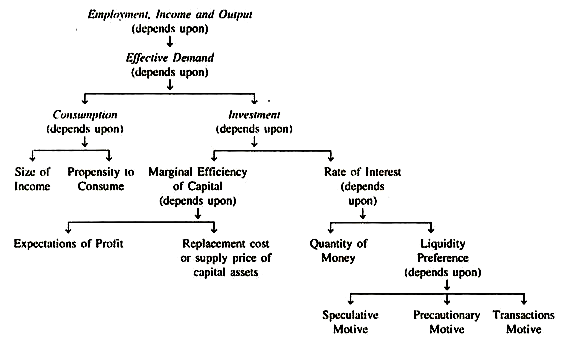
Development of Economic Thought I
This module is the first part of two twin modules teaching the history of economic thought. The aim of this module is to explain and evaluate the evolution of economic thought starting from the Greek times till the mid-nineteenth century and the emergence of Marxist thought.
Although historical, this module contributes in the theoretical economic underpinning of the 2030
Agenda and the role of classical and neoclassical economic theory in this context. Most economic theories – as the 2030 Agenda – are related to
every aspect of sustainability especially those linked to decent work and economic growth (SDG 8), reduced inequality (SDG 10) and peace, justice and strong institutions (SDG 16).
Development of Economic Thought II
This module is the second part of two twin modules focusing on the history and development of economic thought. The aim of this module is to explain and evaluate the evolution of economic thought starting from the end of the first part module namely the emergence of Marxist thought till the contemporary developments in macroeconomics and microeconomics.
Although
historical, this module contributes in the theoretical economic
underpinning of the 2030
Agenda and the role of classical and neoclassical economic theory in
this context. Most economic theories – as the 2030 Agenda – are related
to
every aspect of sustainability especially those linked to decent work
and economic growth (SDG 8), reduced inequality (SDG 10) and peace,
justice and strong institutions (SDG 16).
