This course aims to have students exposed to a wide variety of texts and extracts to acquire knowledge about the differences between the three main literary genres (and their sub-types), through recognition of their technical characteristics. Students are also trained to use literary & critical terminology to produce professional critical analyses of the assigned as well as any other literary texts. Besides aiming at the development of the students’ cognitive & analytical skills, the course also aims to develop their aesthetic & creative faculties in assigning them both critical and creative tasks.
MSA E-Learning
Search results: 193
In INTR405 unit –along with INTR406- students will finally exploit all their expertise and previous experiences acquired throughout their course of study to accomplish their final Interior Design project – The Graduation Project. In these two major units (INTR405 &INTR406) students will execute one final project representing their knowledge, skills and cultural awareness gained in the previous years of study. The student will focus all his/her tools to accomplish the desired outcome.
INTR405: This unit reinforces knowledge and skills in providing students with the practical expertise needed in data gathering, analysis, design program formulation and concept design.
A survey of major authors and works of English literature from the Renaissance period till the beginning of Romanticism. The course is designed to focus on the relation of English literature to the religious, social, economic, and political elements in English culture. The emphasis, however, is upon the significant issues of English literary history and criticism, as reflected in the literature itself.
AIMS This course expands the principles of operating systems introduced in the prerequisite to cover the advanced topics in modern operating systems, memory management subsystems, file systems, concurrency, networks, distributed operating systems, distributed mutual exclusion, distributed deadlocks detection, load balancing, process migration, file management and organization, security and protection, fault tolerance, issues within client/server processing and object orientation. LEARNING OUTCOMES Knowledge On completion of this module, the successful student will be able to: • Demonstrate construction and design of advanced OS components such as: memory management subsystems and file system • Demonstrate basic concepts commonly used in network operating systems and network programming. • Critically appraise the advantages and limitations of peer to peer and server based NOS's. • Categorize and appraise security and protection techniques • Discuss advanced features of OS such as client/server processing, object orientation and fault tolerance Skills This module will call for the successful student to demonstrate: • Provide a critical analysis of commercially produced NOSs from the prespective of suitability for various applications. • Select, implement and manage NOSs. • Select NOS suitable for a particular application. SYLLABUS • File-System Interface. • File-System Implementation. • I/O Systems. • Network Structures. • Distributed System Structures. • Distributed File Systems. • Protection. • Security. • Fault Tolerance. • Client/Server processing and Object Orientation Assessment Scheme • Unseen Examinations 60 % • Coursework 40% Learning materials • Operating Systems Concepts, 8th ed. John Wiley & Sons, became available on July 18, 2008
LU Code : TR 402
Title : Advanced Simultaneous Translation
Level : 4
Credit Hours/Points: 3
Prerequisite: TR 400
Aims:
This module aims to have students grasp the fundamental concepts and techniques common to simultaneous interpretation, apply the skills and techniques of simultaneous interpretation and interpret in the simultaneous mode on general and semi-specialized topics. Over a period of 14 weeks, besides theoretical lecturing, students are exposed to hands-on experience of simultaneous and conference interpretation, through simulations.
The content of the module will comprise the following:
- Public speaking for interpretation purposes
- Listening comprehension
- Exercises in simultaneous interpretation on general and semi-specialized topics.
- Practical Mock Conference interpretation
Learning Outcomes:
Knowledge:
By the end of this module students are expected to demonstrate;
- Understanding of the nature of the work environment, its ethics and protocols.
- Understanding of the physical as well as mental skills required
Skills:
By the end of this module students are expected to demonstrate;
- Further advanced translation skills
- Enhanced language skills
- Adjustment to the work place: composure and confidence under stressful conditions
Learning Materials:
Language and Translation lab
Simulations
Software: TRADOS Translator’s Solution – TMS – TM and An-Nakel – Adobe Audition
Also recordings from regional and local conferences will be used- A Dictionary of Modern Written Arabic by –
References:
-Hans Wehr (Arabic –English) Edited by J. Milton Cowan.
- A Dictionary of Diplomacy & International Affairs ( English-French-Arabic) by Samouhi fawq El'Adah. Published by Librairie du Liban.
- A Dictionary of Modern Political Idioms ( English-French-Arabic) by Magdi Wahba & Wagdi Ghali.
- Baker M. (ed.) 1997 Routledge Encyclopedia of Translation Studies. (
- Basil H. 2001 Teaching and Resarching Translation. (
- Bassnett S 1980/2002 Translation Studies. (
- Baily M (ed.) 1997 The Proceure of The Security Council (3ed). (
- Simons S. 2002 Targeting
- --------- 1996 Gender in Translation: Cultural Identity and the Politics of Translation. (
- Verschueren J. 1999 Understanding Pragmatics. (
- Vincent A. (ed.) 1997 Political Theory: Tradition and Diversity. (
_
-"Language Interpretation". Retrieved from www.wikipedia.org/wiki/Language_interpretation
on 15/9/2011
محمد عناني . نظرية الترجمة الحديثة : مدخل لمبحث دراسات الترجمة. القاهرة, لونجمان (2003).
محمد عناني . مرشد المترجم. القاهرة, لونجمان (2001).
Assessment Scheme:
Students sit a 90 minute mid term exam and a 3 hour final exam. Course work includes oral presentations, analysis and review of peer/other taped simultaneous translation practice, and a final project of live translation practice in a chosen organization.
Assessment Pattern:
Mid term Exam: 20 %
Final exam: 30 %
Coursework: 50%
Learning Unit Contact Hours Per-Week:
Workshops: 90 minutes
Oral Presentations: 3 hours
Total contact hours per semester: 42 hours
Total other study hours per semester: 21 hours
Total study hours per semester: 63 hours
Module Leader:
This course is the first phase of the graduation projects of PR and Advertising. It is mainly the extensive research part. It contains the extensive research part, data collection, data analysis where the students do a survey and analyse the results and relate the results to the already read material.
The research is about a social marketing problem to be solved in the Egyptian society, or about rebranding of an already existing Egyptian entity.
The idea of the research has to be related to the SDGs and the Egyptian sustainable plan 2030.
The students do not only study the problem in the Egyptian society, but also they provide the scientific solutions for it. They are asked to seek professional help from real practitioners in the field to provide real solutions to the problem. This happens through the interviews with practitioners related to the problem.
The same thing applies in the rebranding part, they manage to choose an Egyptian entity and follow the rebranding marketing plan to make it a new different entity.
In both cases, they do huge extensive literature review, similar campaigns and its results, Swot analysis, macro environment, decide on the variables for the survey, conduct the survey, analyse it and come up with solutions.
SDG- This course is a universal repository for all courses at MSA with a large number of potential AI topics.
- Coordinators of different courses at MSA faculties can use any subset of such topics in their respective courses as long as the courses specifications allow (directly or indirectly).
- Coordinators of all courses at MSA faculties are encouraged to import any topic(s), activity(s), and/or resource(s) they like from this course to their respective courses.
This course is designed to enable students to focus on the analysis of the Oscillators, linear and non-linear wave shaping, sweep generator, and voltage regulators.
This
course aims to provide an overview of modern research and industrial
applications of animal cell biology and allow students to explore the
applications of animal cell culture and other technologies in relation to
industry, research, medicine and technology of diseases treatments. The course
also enables students to evaluate the industrial, research and biomedical ideas
associated with animal cell biology.
Dear Students,
- We wish you all a useful and fruitful semester adorned with your rewarding hard work.
- You will find here all the course materials including Lectures, Assignments, Attendance, Links, PDF books and any other announcements related to the course)
- The Instructors for this course are as follows:
Dr Seham Dawoud (E.mail: seahmed@msa.edu.eg)
A.L Mohamed Salah (E.mail: mbadr@msa.edu.eg)
A.L Noha Ismail ( E.mail: neismail@msa.edu.eg)
- You should be informed that all assignments should be delivered on time as late assignments will not be accepted.
- keep in mind that at the end of the semester, you will be asked to submit 2 completed portfolios of all your assignments during the semester one of them will be a hard copy & the other one will be a soft copy (Digital Portfolio) by scanning or photographing your work & upload it to e-learning (each assignment on time).
- In case of an incomplete portfolio, you’ll be deprived of the grades of the missing assignments.
- In case of undelivered portfolio (both Hard & soft copies) you'll be deprived of your coursework grades.
Best of Luck
This course will focus on the basic principles of the Artificial
intelligence (AI), with an overview on the recent Machine learning and Deep
learning applications in Biotechnology. Students will go through multiple open
source toolkit for Artificial neural network construction, protein 3D
structure prediction, and simulations for microbial evolution using smart
algorithms.
أعزائي الطلاب الذين لم يلتحقوا بالاختبار الثاني للكورس ورك والذي مجموع درجاته مع الامتحان الشفوي 20 درجة هذا نداء أخير سأعقد امتحانا لكم يوم الإثنين القادم 23-12 فأرجو التواجد في المحاضرة في قاعة A113
من الساعة 2- 3ونصف وهذه فرصة أخيرة لكم لتحسين وضعكم . كما أطالب جميع طلابي بعمل تقييم المادة الذي أرسل لكم عبر الميل لأن تقييمكم يهم الجامعة وإدارة الجودة.
مع خالص تقديري
د/ شيرين العدوي
قصيدة شنق زهران/ صلاح عبد الصبور([i]):
وثوى في جبهة الأرض الضياء
ومشى الحزن إلى الأكواخ
تنين
له ألف ذراع
كل دهليز ذراع
من أذان الظهر حتى الليل
يا الله
في نصف نهار
كل هذي المحن الصماء
في نصف نهار
مذ تدلى رأس زهران الوديع
· * *
كان زهران غلاما
أمه سمراء
والأب مولد
وبعينيه وسامة
وعلى الصدغ حمامة
وعلى الزند أبو زيد سلامة
ممسكا سيفا، وتحت الوشم نبش كالكتابة
اسم قرية
(دنشواي)
شب زهران قويا
ونقيا
يطأ الأرض خفيفا
وأليفا
كان ضحاكا ولوعا بالغناء
وسماع الشعر في ليل الشتاء
ونمت في قلب زهران زهيرة
ساقها خضراء من ماء الحياة
تاجها أحمر كالنار التي تصنع قبلة
حينما مر بظهر السوق يوما
ذات يوم ...
واشترى شالا منمنم
ومشى يختال عجبا، مثل تركي معمم
ويجيل الطرف .... ما أحلى الشباب
عندما يصنع حبا
حينما يجهد أن يصطاد قلبا
· * *
كان يا ما كان
أن زفت لزهران جميلة
كان يا ما كان
أن مرت لياليه الطويلة
ونمت في قلب زهران شجيرة
ساقها سوداء من طين الحياة
فرعها أحمر كالنار التي تحرق حقلا
عندما مر بظهر السوق يوما
ذات يوم
مر زهران بظهر السوق يوما
ورأى النار التي تحرق حقلا
ورأى النار التي تصرع طفلا
كان زهران صديقا للحياة
ورأى النيران تجتاح الحياة
مد زهران إلى الأنجم كفا
ودعا يسأل لطفا
ربما ...... سورة حقد في الدماء
ربما استعدى على النار السماء
وضع النطع على السكة والغيلان جاؤوا
وأتى السياف مسرور وأعداء الحياة
صنعوا الموت لأحباب الحياة
وتدلى رأس زهران الوديع
قريتي من يومها لم تأتدم إلا الدموع
قريتي من يومها تأوي إلى الركن الصديع
قريتي من يومها تخشى الحياة
كان زهران صديقا للحياة
مات زهران وعيناه حياة
فلماذا قريتي تخشى الحياة
تظهر بوضوح البنية السردية في قصيدة "شنق زهران" للشاعر المصري صلاح عبد الصبور، مثل السارد والشخصيات والزمان والمكان والحدث....إلخ.
وقد كان السارد بالضمير الثالث "هو" نسقا معتمدا في هذه القصيدة، فهو سارد خفي يراقب الأحداث ولا يشترك فيها.
وهو سارد عليم بسرده، ولا يخبرنا من أين جاء بالمعلومات في هذه القصيدة، مما يطلق العنان لخيالنا كي نتصور قربه الشديد جدا من زهران وعالمه، سواء كان هذا القرب بالقراءة والمعرفة أم كان بالمعايشة والمجاورة، ولكننا نعلم من خارج النص أن الشاعر صلاح عبد الصبور ولد بعد شنق زهران بأكثر من عقدين من الزمان.
وفي هذه القصيدة يتم التركيز على الشخصية المحورية تركيزا هائلا.
وهذه الشخصية لها اسم محدد هو زهران، مما يوحي بالجمال والنقاء، وكأنه نجم لامع، أو شجرة مزهرة، ويمنحه الشاعر صفات مؤثرة في المتلقي، مما يجعل إحساسه بالمصاب في فقده فادحا، لأن زهران هنا يمثل قيمة إتسانية في غاية النبل والصفاء، فهو شاب قروي، ومن المعروف أنه شخصية حقيقية من الذين تم إعدامهم أمام أهاليهم على يد المحتل الإنجليزي الغاصب في جرن القرية ــ قرية دنشواي بمحافظة المنوفية ــ موقع الحادثة الشهيرة التي تعرف في التاريخ بــ "حادثة دنشواي"، عام 1906م.
وقد تم شنقه وهو في مرحلة الشباب والفتوة، وحالته الجسدية قوية جدا، فزنده مفتول، كما أنه يسير خفيفا وأليفا، وحالته النفسية متزنة، ولكن تبدو مسحة من التيه وحب الحياة الشديد.
وقد رصدته كاميرا الذات الشاعرة، وركزت على التفاصيل الصغيرة التي تمنح إحساسا شعريا بعيد الغور، وهذه التفاصيل الصغيرة هي موطن ذو أهمية كبيرة في السرد، كما بدت الحركة الزمنية المتماسكة بوضوح شديد في هذه القصيدة، والحقيقة أن هذه القصيدة يظهر فيها التماسك النصي بوضوح شديد، والتمساك النصي يتجلى من خلال الصورة الشكلية والصورة الدلالية، والصورة الشكلية "تعني" ترابط الجمل في النص مع بعضها البعض بوسائل لغوية معينة .. والثانية تهتم بالمضمون الدلالي في النص، وطرق الترابط الدلالية بين أفكار النص من جهة، وبين معرفة العالم من جهة ثانية"([ii]).
فالقصيدة تبدأ من النهاية، بعد ذلك تقوم بعملية ارتداد كبرى حتى تصل إلى لحظة النهاية وما بعدها، مما منح القصيدة تماسكا سرديا واضحا.
فالمقطع الذي بدأت به القصيدة، وهو:
وثوى في جبهة الأرض الضياء
ومشى الحزن إلى الأكواخ
تنين
له ألف ذراع
كل دهليز ذراع
من أذان الظهر حتى الليل
يا الله
في نصف نهار
كل هذي المحن الصماء
في نصف نهار
مذ تدلى رأس زهران الوديع
يصور نهاية زهران، وقبل هذا المقطع كان العنوان هو "شنق زهران"، وهو يتكون في كلماته الظاهرة من كلمتين، وهاتان الكلمتان بينهما علاقة قوية جدا هي علاقة الإضافة، الأولى "شنق" والثانية "زهران"، فكلمة الشنق تثير في نفس المتلقي الكثير من الشجون والألم، لأنها تستدعي الموت العنيف، عن طريق الضغط بحبل محكم حول الرقبة حتى الموت، وهذا الشنق يضاف لشخصية رجالية هي زهران.
يبدأ هذا المقطع الملحمي بواو العطف وواو العطف تعطف المعطوف على المعطوف عليه، ومن هنا فإن هذه القصيدة تبدأ قبل بدايتها، لأنها تنهض بتنشيط ذهن المتلقي لملء فجوات سردية لم يملأها الشاعر حتى الآن، وعلى المتلقي أن يستغل العنوان الذي يستحضر الشنق لشخصية إنسانية هي زهران ويستغل أيضا معلوماته الخارجية عن مذبحة دنشواي عام 1906م ليسكن المتواليات السردية في ذهنه المنظم.
بعده يتبعه فعل ماض هو ثوى، بما يستدعيه من السكون التام وعدم الحركة، ويستدعي المثوى الأخير، ولكننا نفاجأ أن الذي ثوى في جبهة الأرض هو الضياء، بما تستدعيه كلمة جبهة من شموخ، فهناك شموخ في الموت، وكان من نتيجة ذلك أن تأتي متوالية سردية، يظهر فيها الحزن، وهو يمشي إلى الأكواخ، بل إن هذه المتوالية السردية تؤسطر الحزن، فتجعله تنينا له ألف ذراع، مما يوحي بجبروته وقسوته وثقله الهائل على أكواخ القرية، وتمدده الرهيب، وهو بأذرعه الأسطورية المخيفة المتوحشة يتوغل في كل مكان، ويحدد الشاعر زمنا لهذا الحزن الرهيب، وهو من أذان الظهر حتى الليل، أي في نصف نهار ظهرت كل هذه المحن الصماء، ووصف المحن بأنها صماء له دلالة، وكأن صراخ أهل القرية الإنساني أمام هذه المحن لم يجد منها أذنا تسمع، فهي أذن صماء تماما، لا تبالي بآلام المطحونين، وهنا تنهض الاستعارة بدورها الدلالي والجمالي داخل الخط السردي للقصيدة، فقد تحولت هذه المحن وهي لا حي إلى كائن حي، ولكنه فقد أهم ما كينونته الحيوية، وهو الاستماع الرحيم لآلام الآخرين، وحتى هذه اللحظة لا نعرف السبب الذي جعل كل ذلك يحدث، وإن كان العنوان يدخلنا في الحالة المأساوية منذ البداية، حتى تأتي الجملة الكاشفة والمفسرة لما حدث، وهي:
"مذ تدلى رأس زهران الوديع".
وتنهض حروف المد بدورها في التنفيس عن الألم الرهيب المكبوت.
ومن هنا فإن القارئ يدخل في قلب المأساة منذ البداية، وتلعب تقنية النجوم دورا كبيرا في منح القارئ هدنة يلتقط فيها أنفاسه، ويحاول أن يستوعب هذه الجملة السردية الكابوسية، والتي تراسلت تماما مع عنوان القصيدة، ويعد تركيز الضوء على رأس زهران وهو يتدلى متوائما مع جبهة الأرض من قبل، ومتوائما مع الضياء أيضا.
ولا شك أن الجملة السردية السابقة تنهض بتحفيز حس السؤال لدى المتلقي، لأنه أصبح يود الإشباع السردي عن هذه الشخصية، فقد تم ذكرها حتى الآن مرتين: المرة الأولى في العنوان: شنق زهران، والمرة الثانية في جملة تدلى رأس زهران الوديع، وكان من نتيجة هذا الشنق وذلك التدلي لرأس زهران أن ثوى الضياء في جبهة الأرض وأن مشى الحزن الرهيب الثقيل عبر أكواخ القرية ودهاليزها وأطبق الحزن الشامل عليها، وهنا قد يجد المتلقي أن ما يحدث نتيجة هذا الشنق أكثر مما ينبغي، ولذا كان لابد من تدخل الذات الساردة لكي تفعّل الاقتناع التام بهذا الحزن الكبير، ذلك الذي وضعتنا في قلبه دون سابق تمهيد، ولذا رأينا عملية الارتداد الكبيرة في المقطع التالي، وذلك بعد وقفة نهضت بها تقنية النجوم.
وقد رسمت الذات الشاعرة بحرفية الفنان صورة مفعمة بالحياة لزهران الذي تدلى رأسه الوديع في المقطع الأول. وهنا ينهض الوصف بوظيفة ذات أهمية بالغة، وهي الوظيفة "التفسيرية الرمزية في الوقت نفسه، فالصور الجسدية وأوصاف اللباس والتأثيث تتوخى .. إثارة نفسية الشخوص وتبريرها في نفس الآن، تلك الشخوص التي هي بمثابة علامة وعلة (سبب) ونتيجة دفعة واحدة"([iii]).
ويبدأ الارتداد الخارجي منذ أن كان زهران غلاما، أي في مرحلة عمرية ممعنة في الماضي، يقول:
كان زهران غلاما
أمه سمراء
والأب مولد
وبعينيه وسامة
وعلى الصدغ حمامة
وعلى الزند أبو زيد سلامة
ممسكا سيفا، وتحت الوشم نبش كالكتابة
اسم قرية
(دنشواي)
يظهر الهدف من السرد بوضوح منذ البداية، وهذا الهدف يتمثل في عملية معايشة ممتدة للشخصية التي تفاجأ المتلقي بوجودها في عالمه دون سايق معرفة حقيقية، وهذه المعايشة تهدف إلى استمالة القارئ لكي يكون حزنه هائلا بسبب الموت العنيف الذي تعرضت له الشخصية المحورية، وبالتالي لا يجد غضاضة في جثوم تنين الحزن على أنفاس القرية كلها.
والسطور السردية السابقة تتسم ببطء الحركة، لأنها تنتمي إلى عالم الوصف، وهذا الوصف نهض بدوره في تثبيت الصورة للشخصية المحورية صاحبة المأساة، فزهران أمه سمراء، وهنا يكتسب اللون أهمية فائقة، فالأم سمراء، مما يشير إلى عملية التداخل بين الأم من ناحية وأرض مصر من ناحية أخرى، فمنذ التاريخ الممعن في القدم ومصر هي "كمت" أي الأرض السمراء، وهذا يدل على مدى ارتباط زهران الوثيق بأرض الوطن، كما أن الجمل السردية التعريفية تتوالى بكثرة فالأب مولد، وهناك وسامة في عينيه، ومن المعروف أن العينين هما منفذ الروح على العالم، فإذا كانت هناك وسامة في عينيه فإن روحه تتميز بالوسامة أيضا، ثم تمعن الذات الساردة في نقل تفاصيل صغيرة تكشف بوضوح شديد عن طبيعة البيئة التي يعيش فيها زهران، حيث تهتم القرية المصرية خصوصا في فترة حادثة دنشواي بالوشم، وهنا تضخ الذات الشاعرة متواليات سردية تكرس في هذا الاتجاه، فعلى الصدغ، وهو جزء من الوجه حمامة/ رمز السلام الذي يتمتع به أبناء هذا الوطن، وعلى الزند أبو زيد سلامة ممسكا سيفا، وربما كان ذكر الحمامة على الصدغ يشير إلى ضعف الشخصية وانسحابها من هذا العالم، ولذا جاءت صورة الفارس الممسك بالسيف والمرسوم على زنده، لتشير إلى قوة الشخصية وفروسيتها، فالسلام يحتاج إلى قوة تحميه، واختيار أبو زيد يحمل دلالة خاصة فهو بطل شعبي له في وجدان الجماهير مكانة خاصة، خصوصا أبناء القرية منهم. هؤلاء المفتونون بالسير الشعبية عموما، وسيرة تغريبة بني هلال وبطلها أبو زيد الهلالي خصوصا، ثم تضخ الذات الشاعرة متوالية سردية أخرى، وهي وتحت الوشم نبش كالكتابة اسم قرية دنشواي، وهنا تتوحد الشخصية المحورية مع وطنها المتمثل في قرية دنشواي، ويتم استدعاء التاريخ الفرعوني من خلال ذكر النبش والكتابة مما يدل على أن هذا البطل يختزن في داخله تاريخ أمته.
وهنا يظهر بوضوح شديد أهمية الوصف في توقيف الزمن، مما جعل المتلقي يعايش الشخصية المحورية أطول فترة ممكنة، فتنشأ في داخله صلة نفسية معها، ثم تقفز الحركة الزمنية قفزة كبيرة لينتقل السرد بنا من مرحلة الصبا للشخصية إلى مرحلة الشباب، وهذه القفزة الزمنية تمثل فجوة زمنية يستطيع المتلقي أن يملأها بخياله.
يقول:
شب زهران قويا
ونقيا
يطأ الأرض خفيفا
وأليفا
كان ضحاكا ولوعا بالغناء
وسماع الشعر في ليل الشتاء
نجد القفزة الزمنية واضحة بين هذه السطور وما قبلها، فقد كان زهران غلاما، واليوم شب زهران قويا ونقيا، ويبدو بوضوح شديد انحسار الانزياحات اللغوية التي كنا نجدها في القصيدة الاستعارية، والتقاط صور واقعية بسيطة ولكنها بعيدة الغور، حيث ينحسر الأسلوب الاستعاري الذي يعتمد على التحويل مفسحا المجال للأسلوب الكنائي المعتمد على المجاورة ذلك الذي نراه متحققا في السرد، وقد لعبت صيغة المبالغة دورا كبيرا في بث ملامح زهران النفسية والجسدية، فهو قوي ونقي وأليف وخفيف وضحاك وولوع بالغناء وسماع الشعر في ليل الشتاء، وكلها تجعل من زهران شخصية محبة جدا للحياة وما فيها من شغف، وبعد ذلك يقول:
ونمت في قلب زهران زهيرة
ساقها خضراء من ماء الحياة
تاجها أحمر كالنار التي تصنع قبلة
يبدو بوضوح شديد التفاعل مع البيئة والامتياح من مفرداتها في القصيدة السردية، فقد نمت في قلب زهران زهيرة، وهنا يلعب اللون دورا كبيرا في الدلالة، فالزهيرة ساقها خضراء، بما يوحي به اللون الأخضر من خصوبة وحيوية دافقة، ويستدعي مرحلة الشباب وما فيها من ازدهار، ويأتي اللون الأحمر في قوله:
تاجها أحمر كالنار التي تصنع قبلة، وإذا كان اللون الأحمر والنار يستدعي الحريق في الكثير من التصور[l1] فإن النار هنا هي جوهر الحياة وقدرتها على التجدد، لأنها لون نار العشق والهوى، فهي هنا نار إيجابية.
يقول:
حينما مر بظهر السوق يوما
ذات يوم ...
واشترى شالا منمنم
ومشى يختال عجبا، مثل تركي معمم
ويجيل الطرف .... ما أحلى الشباب
عندما يصنع حبا
حينما يجهد أن يصطاد قلبا
وهنا لقطة تصور حركة الشخصية المحورية، وما يصاحب هذه الحركة من خصوبة وحيوية دافقة، وتلعب التفاصيل الصغيرة دورا فائقا في بث دلالات بعيدة الغور، ويأخذ الشال المنمنم مركز ثقل واضح في هذا السياق، وتظل الصور المجازية في حالة انحسار واضح، ولكن يظهر التشبيه في قوله:
ومضى يختال عجبا مثل تركي معمم، وهذا التشبيه يشير إلى سياق له دلالة، حيث كانت مصر واقعة في هذه الفترة تحت الاحتلال الإنجليزي من ناحية والسيطرة التركية الصورية عليها من ناحية أخرى، ولذا فقد كان للأتراك حضور كبير على الساحة المصرية، وكان معظمهم يتمتعون كثيرا بخيرات مصر، في حين كان أبناؤها المنتجين الحقيقيين لا يتمتعون بشئ، وكان أقصى طموح أحدهم أن يمر بالسوق ويشتري شالا منمنما يجعله يتيه من الفخار مثل التركي المعمم رمز الغنى والجاه والأبهة، لكم كانت هذه الشخصية في غاية البساطة، ولكنها في الوقت نفسه في غاية الحب للحياة وفي غاية الخصوبة والحيوية.
ومن هنا فإن خصوبته وحيويته هي ما يغري به، فهو يصطاد قلبا بشبابه وليس بماله ولا بسلطته أو جاهه.
وإذا كانت هذه السطور تنتج الدلالة في جانب الفرح وحب الحياة فإن القارئ لا يستطيع أن يتلقاها وهو في حالة من الخدر اللذيذ، وإنما يتلقاها في ضوء ما تلقاه من سرد سابق كرس لحدوث الفجيعة كأقسى ما تكون، فيتشكل في ذهن المتلقي خطان مختلفان: خط الموت المفجع وخط الخصوبة الدافقة، وإذا كان خط الموت المفجع قد تلقاه القارئ منذ البداية فإن خط الخصوبة المتدفقة لا يزال في طور التشكل، وتشكله هذا يجعل خط الموت للشخصية المحورية/ زهران أكثر مأساوية من ذي قبل، لأن القارئ أصبح يعرفه أكثر، فيقول:
كان يا ما كان
أن زفت لزهران جميلة
كان يا ما كان
أن مرت لياليه الطويلة
تحضر سمات الحكي الشعبي في قوله "كان يا ما كان"، وهي سمة لها حضور كبير حينما تتم أسطرة الحكاية، وانعتاقها من المحددات الزمانية والمكانية ليتم الحكي الذي يمتد عبر الأزمان والأماكن، والتركيز على الحكاية فقط، وهنا ينجح زهران في اصطياد قلب عامر بالشوق والجمال، وتمر لياليه ذات الطول الفائق، والقارئ يتلقى السرد في هذه القصيدة وقد أصبح مهيئا للاقتناع بتوالي الجمل السردية، فزهران ذو الخصوبة والحيوية الدافقة والشباب الحلو نجح بعد جهد في اصطياد قلب، وكان سر نجاحه هو استجابته لنداء قلبه الشاب وجسمه الغض فبذل الجهد الكافي من أجل الحب، وكان شبابه وبساطته الآسرة وحيويته الدافقة هي السر الذي جعل هذا القلب يقع في شباكه الذهبية، وهنا تأتي المتواليات السردية لتكشف عن تطور الحدث السردي، فيقول:
ونمت في قلب زهران شجيرة
ساقها سوداء من طين الحياة
فرعها أحمر كالنار التي تحرق حقلا
ويتم تكرار نفس الأفعال والصيغ والجمل ولكن بتحريف بسيط، ولكن هذا التحريف البسيط يحول مؤشر الدلالة إلى النقيض، وإذا كان في السابق قد نمت في قلب زهران زهيرة، فإنه الآن قد نمت في قلبه شجيرة، وهنا يتم أيضا استغلال الألوان في إنتاج الدلالة، فساق الشجيرة هنا سوداء، بما يضخه اللون الأسود من دلالة التشاؤم، وفرع هذه الشجيرة التي نمت في قلب زهران أحمر، وإذا كان اللون الأخمر مع الزهيرة كان من الشوق والهوى فإنه هنا من الحريق الذي يلتهم الحقل / رمز خصوبة الحياة. وهنا يبدأ التراسل مع عنوان القصيدة ومع المقطع الأول منها، وأصبح القارئ يتوقع حدوث الكارثة، ولا تخفى بطبيعة الحال دور أدوات الربط اللغوية في تماسك الحدث السردي، وهنا يكتس حرف العطف "الواو" أهمية كبيرة جدا.
وإذا كانت البنية التشبيهية متراسلة مع بنية تشبيهية سابقة فإن انحرافها بدا واضحا جدا، فتاج الزهيرة التي نمت في قلب زهران شبهه الشاعر بالنار التي تصنع قبلة، ولكن هنا نجد فرع الشجيرة التي نمت في قلب زهران كالنار التي تحرق حقلا، وما أبعد الفرق بين النار هناك والنار هنا، فالنار هناك كانت نارا إيجابية هي نار الحب والشهوة، وهذا هو صميم الحياة وقلبها النابض، والنار هنا هي تلك النار التي تحرق الحقل/ رمز الخصوبة والحيوية ولذا فالنار هنا هي تلك النار الحارقة المهلكة، وهنا يتواءم ما يعرفه المتلقي عن حادثة دنشواي الشهيرة التي حدثت عام 1906م، وكان من مظاهرها القوية نشوب الحريق في جرن من أجران القمح، مما جعل الأهالي يطاردون الجنود الإنجليز الذين تسببوا في هذا الحريق لمحصولهم الذي جاء بعد شهور من الكد والعرق، وبعد طول انتظار له، لأنه يمثل لهم أهمية فائقة في حياتهم.
وقد نهضت البنية التشبيهية هنا بتحول مفصلي في سرد القصيدة، جعلها تغادر جوانب التفاؤل والحيوية ليدخل بنا الشاعر/ السارد في طريق مسدود، هو طريق الموت العنيف الذي كان من نصيب الشخصية المحورية فيها.
وبدأ المتلقي يعيش في جو النار الحارقة بعد أن كان يعيش في جو النار الخصيبة إن صح هذا التعبير.
وهنا تأتي الجمل السردية المعبرة عن جو النهاية، فيقول:
عندما مر بظهر السوق يوما
ذات يوم
مر زهران بظهر السوق يوما
ورأى النار التي تحرق حقلا
ورأى النار التي تصرع طفلا
كان زهران صديقا للحياة
ورأى النيران تجتاح الحياة
ويتكر مرور زهران بالسوق يوما ذات يوم، ولكن شتان بين مروره في القديم، وقد اشترى شالا منمنما واختال عجبا بنفسه مثل تركي معمم، واستطاع بفتوته وشبابه أن يصطاد قلبا جميلا ومروره الآن وقد واجه الكارثة، وعليه أن يتخذ موقفا، فقد رأى النار رمز الجحيم تجتاح الحقل رمز الحياة، بل رآها تصرع طفلا رمز مستقبل الوطن، ورمز الحياة المتجددة على أرض هذا الوطن، وزهران صديق الحياة، وها هو يرى النيران ــ جمع النار فقد توالدت وكثرت في لحظة ــ تجتاح الحياة.
كل هذه الجمل السردية تميل بجانب المتلقي لمعرفة اختيار زهران للفعل الذي سيقوم به، ومن هنا فقد:
مد زهران إلى الأنجم كفا
ودعا يسأل لطفا
ربما ...... سورة حقد في الدماء
ربما استعدى على النار السماء
فقد لجأ إلى السماء أولا كي تقف بجانب الحياة ضد هذه النيران الغاشمة، ودعاها يسألها اللطف، واستعداها على النار.
وتظهر سقطة البطل التراجيدي، فعلى الفور:
وضع النطع على السكة والغيلان جاؤوا
وأتى السياف مسرور وأعداء الحياة
صنعوا الموت لأحباب الحياة
وتدلى رأس زهران الوديع
فبسرعة فائقة وضع النطع على السكة، وبسرعة فائقة جاء الغيلان وبسرعة فائقة أتى السياف مسرور وأعداء الحياة وبسرعة فائقة صنعوا الموت لأحباب الحياة، وبسرعة فائقة تدلى رأس زهران الوديع.
وهنا تكتسب السكة ثقلا دلاليا واضحا، فقد تم التنفيذ في موقع الحادث، وأمام عيون الجميع، وأمام الأهل والأطفال، وتستحضر الذات الساردة تاريخا عريضا من الظلم حينما تستدعي السياف مسرورا رمز آلة تنفيذ البطش بالأبرياء.
ويكشف الشاعر عن وحدة القهر والعسف عبر الأزمان والأماكن، فمسرور الذي اكتسب شهرة بالعسف والجبروت في العصور الوسطى يظهر الآن بسرعة فائقة في العصر الحديث وينهض بأفعال العسف نفسها رغم اختلاف الزمان والمكان والحضارة.
وهنا تلعب المقابلة دورا كبيرا في الكشف عن الصراع بين جانبين مختلفين: جانب الموت وجانب الحياة.
وتكتسب الصفة أهمية كبيرة (رأس زهران الوديع) فالآن يدرك المتلقي بقناعة تامة صفة الوداعة، ويتفاعل أكثر وبأثر رجعي مع هذه الصفة التي ذكرت من قبل في المقطع الأول، ولكنه استقبلها فجأة، أما ذكرها مرة ثانية هنا فقد تفاعل معها وعايش الشخصية منذ الصبا وحتى موتها العنيف فعرف بقناعة تامة أنه ضحية لهؤلاء الغيلان البشعين.
وهنا تظهر بداية القصيدة مرة ثانية، ولكن بعد أن نهضت عملية الارتداد الكبرى بالإضاءات السردية الكاشفة لكل ما بتعلق بالشخصية المحورية ونهايتها المفجعة.
وكان من المتوقع أن تنتهي القصيدة عند هذا الحد، فيكون السرد دائريا مكتملا، ولكن الذات الشاعرة تنطلق بسردها إلى ما بعد موت الشخصية المحورية لتلقي الضوء على القرية التي تجسد فيها الوطن كله فيقول:
قريتي من يومها لم تأتدم إلا الدموع
قريتي من يومها تأوي إلى الركن الصديع
قريتي من يومها تخشى الحياة
كان زهران صديقا للحياة
مات زهران وعيناه حياة
فلماذا قريتي تخشى الحياة
وهنا القرية/ الوطن في حالة حزن منذ رحيل زهران، وهذا ما يرفضه الشاعر، فزهران نفسه كان صديقا للحياة، بل إنه وهو يموت كانت عيناه حياة، فلماذا قريتي تخشى الحياة؟
والحقيقة أن موت زهران لم يجعل القرية تخشى الحياة، فرغم العسف والقهر فإن دماء زهران لم تذهب هباء، وإنما كافحت القرية/ الوطن حتى استطاعت أن تطرد هؤلاء الغاصبين. ومن هنا فإنه على الرغم من وجود المأساة في هذه القصيدة وإطباقها بمقابض من فولاذ على الروح العام فإن الذات الشاعرة ترفض الاستسلام لهذ الحزن، وتنهي القصيدة بسؤال يحمل الكثير من التعجب، وهو فلماذا قريتي تخشى الحياة؟
وهذا السؤال يحمل نغمة صاعدة، هي آخر ما يستقر في ذهن القارئ، وقد نهض بعملية تحول من الأساليب الخبرية المتوالية إلى الأسلوب الاستفهامي المتصاعد، وهيمنة الأساليب الخبرية بصورة كثيفة جدا، وهيمنة الجملة الفعلية ذات الفعل الماضي بصورة كثيفة جدا كان تجليا واضحا لطبيعة البنية السردية في هذه القصيدة.
وتبدو سمة الترابط بوضوح في هذا النمط من الشعر، فالمتواليات فيها مترابطة كي تجعل منها قصة مكتملة الأركان، وكان للمتواليات الإخبارية دور واضح في هذا السياق، في حين انحسرت بصورة واضحة المتواليات الإنشائية.
ومن المعروف أنه "تتألف الجملة من مستويين في بنية الخطاب: إخبارية وإنشائية، ومنها تتفرع ألوان الخطاب من الإخبار إلى الإنشاء، وذلك وفق الفاعلية الشعرية التي تكمن في طبيعة العلاقات اللغوية على مستوى الخطاب ككل، وتشاكلها وتباينها، وانتقال الخطاب من الإخبار إلى الإنشاء، والرجوع إلى الإخبار مرة ثانية، والغاية من ذلك خلق فاعلية شعرية ناتجة من خرق الأنساق الأسلوبية السابقة وإنتاج أنساق أسلوبية جديدة، ثم الانزياح عنها مرة أخرى"([iv]).
من خلال ما سبق تبدو ملامح السرد بوضوح شديد داخل هذه القصيدة "شنق زهران" للشاعر المصري صلاح عبد الصبور، فقد كان النمط المهيمن للسارد هو السارد غير المشارك الذي يستخدم الضمير الثالث "هو" في السرد، وكانت الشخصية المحورية في النص هي شخصية زهران، وهي شخصية لها وجود خارج النص أيضا، فقد كان أحد الذين تم إعدامهم أمام أهلهم في مذبحة دنشواي، وقد تتبعتها كاميرا السرد عبر مراحل مختلفة من عمرها، وهذا التتبع أسهم بشكل كبير في عملية معايشة القارئ لهذه الشخصية، مما جعل مأساة موته مؤثرة جدا بل وفاجعة جدا، "فزهران في مشهدين، الأول عكس مقدار البراءة والرغبة في الحياة والإقبال عليها، والثاني يعكس مقدار الفزع الذي ترك بصمته على الأشياء وعلى الحالة النفسية للشخصية، فالزهيرة .. تحولت إلى شجيرة، والتاج أصبح فرعا، واللون الأخضر المشبع بماء الحياة أصبح أسود مصبوغا بطينها، واللون الأحمر المتأجج بالعاطفة أصبح نارا حارقة لكل ما هو حي أو أخضر، وأصبح الحزن يغمر نفس زهران ونظرته للحياة، أصبح كل شئ يشيخ ويهرم"([v]).
وكانت هناك شخصيات أخرى في القصيدة، شخصيات تقف إلى جانب الشخصية المحورية وشخصيات تقف ضدها، وهي في الغالب شخصيات عامة، ليست محددة مثل الغيلان والسياف مسرور وأعداء الحياة، وكلها شخصيات مضادة للبطل المحوري، وكانت هناك شخصيات صديقة للبطل المحوري مثل جميلة التي زفت له، ومثل أحباب الحياة ومثل أطفال زهران، ولكن الغيلان استطاعوا إنهاء حياة زهران بطريقة عنيفة جدا.
وكان المكان المحوري هو قرية دنشواي، وهي قرية في محافظة المنوفية شهدت حادثة دنشواي المدوية، فهي قرية في الدلتا بما فيها من ملامح، الاتساع/ الحقول/ الحيوانات/ الطيور/ الطوب اللبن الذي تبنى منه البيوت في تلك الفترة/ الفلاحين البسطاء وما بينهم من علاقات.
وعلى الرغم من بساطة القرية والقهر الذي يعيش فيه سكانها فإنها هي المنتج الحقيقي للغذاء الذي يقوم عليه أود الناس، سواء في القرية أم في المدينة، ومن هنا فهذا المكان منتج وعظيم الفائدة.
أما عن الزمان في هذه القصيدة السردية، فقد تفاعل مع سمات زمنية خارجية، هي أواخر القرن التاسع عشر وبدايات القرن العشرين، فمن المعروف أن حادثة دنشواي الشهيرة وقعت عام 1906م في عهد الاحتلال الإنجليزي لمصر، وقد كان هذا الزمن هو نهاية الشخصية المحورية، وقد تفاعلت القصيدة مع فترات زمنية مختلفة من حياته، منذ أن كان غلاما، مرورا بفترة شبابه وزواجه وإنجابه ونهاية بموته المروع.
أما الزمن الداخلي في هذه القصيدة السردية فقد تراواح بين التوافق الزمني الذي ظهر في بداية القصيدة، وقد غلبت عليه سمة نقل الحدث الرهيب، بصورة مشهدية غير متطورة زمنيا، ولكن المقطع الثاني جاء من خلال عملية ارتداد كبرى، بدأت منذ أن كان زهران غلاما حتى وصلت إلى لحظة بداية القصيدة، أي مشهد شنقه المروع، ثم انطلق الزمن بنا إلى ما بعد نهاية الشخصية المحورية.
وكان لهذا التفاعل مع الزمن دور كبير في ضخ متواليات سردية تعرّف بالشخصية المحورية تعريفا عميقا يجعل المتلقي يتفاعل مع موتها المأساوي بصورة قوية.
وكان الوصل بالعطف للمتواليات في هذه القصيدة ذا هيمنة واضحة، مما حقق لهذه القصيدة سمة الترابط.
وعلى الرغم من السرد المحكم والحكاية المكتملة فإن هذه القصيدة السردية قد جمعت إلى جانب السرد فيها سمات تنتمي إلى عالم الشعر انتماء واضحا، مما جعل القصيدة مطعمة بهذين الفنين بصورة واضحة.
وقد ظهر من سمات الفن الشعري فيها انتماؤها إلى فن الشعر، فقد نشرت في ديوان شعري ضمن قصائد لشاعر شهير جدا في العصر الحديث هو الشاعر المصري صلاح عبد الصبور، ومن هنا ظهرت القصدية أي قصدية الشاعر وإعلانه أن يكتب قصيدة وليست قصة.
الملمح الثاني من ملامح فن الشعر هو المحافظة على الوزن الواحد، وذلك من خلال ما يعرف بقصيدة التفعيلة، أو ما اصطلح على تسميته بالشعر الحر، والمحافظة على الوزن سمة تنتمي للفن الشعري، بل إنها من أهم ملامحه، كما ظهر ملمح آخر من ملامح فن الشعر وهو حضور القافية حضورا واضحا، والقافية في هذه القصيدة ليست هي القافية الموحدة كما نراها في القصيدة العمودية، وإنما هي قافية تتردد بمقدار ما يحتاجه النص، وتتغير أيضا بمقدار ما يحتاجه النص، ولكنها تظل حاضرة من البداية وحتى النهاية.
ومن ملامح الفن الشعري أيضا في هذه القصيدة حضور الجانب التصويري مثل "ثوى في جبهة الأرض الضياء"
"مشى الحزن إلى الأكواخ تنينا له ألف ذراع"
"كل دهليز ذراع"
فهذه انزياحات تكرس لفن الشعر أكثر من أي فن آخر.
كما نجد من ملامح فن الشعر عنصر التكثيف في الصورة.
وتتخذ الذات الشاعرة من بنية التكرار تقنية معتمدة في القصيدة، وهذه البنية تنهض بدور إيقاعي واضح يكرس لملامح الفن الشعري بقوة، وقد كانت بنية التكرار ذات تجليات مختلفة، منها تكرار الحرف الذي سجل حضورا قويا، على نحو ما نجد في قوله:
مر زهران بظهر السوق يوما
ورأى النار التي تحرق حقلا
ورأى النار التي تصرع طفلا
نجد تكرارا كبيرا لحرف الراء في السطور السابقة، فقد تكرر هذا الحرف تسع مرات في ثلاثة أسطر قصيرة، مما جعله يسجل كثافة واضحة.
كما تكررت الكلمة أيضا وتكرر أكثر من الكلمة مثل "ورأى النار التي"
كما تكررت الصيغ مثل صيغة الفعل المضارع المبدوء بتاء، مثل تحرق/ تصرع، ومثل الاسم المنصوب يوما/ حقلا/ طفلا.
كل هذا التكرار الكثيف يعد سمة محورية من سمات فن الشعر، ومن هنا فإن التداخل بين فن الشعر من ناحية وفن القص من ناحية أخرى يظل حاضرا بقوة في هذه القصيدة السردية للشاعر المصري صلاح عبد الصبور.
[i] صلاح عبد الصبور، الديوان، الأعمال الكاملة، دار العودة، بيروت، ط1، 1973م، ص18..
[ii] انظر جمعان عبد الكريم، إشكالات النص، دراسة لسانية نصية، ـ النادي الأدبي بالرياض، ط1، 2009م، ص222 ــ 223.
[iii] جيرار جينيت، حدود السرد، ترجمة بنعيسى بو حمالة، ضمن كتاب طرائق تحليل السرد الأدبي، منشورات اتحاد كتاب المغرب، الرباط، ط1، 1992م، ص77..
[iv] يوسف إسماعيل، البنية التركيبية في الخطاب الشعري، قراءة تحليلية للقصيدة في القرنين السابع والثامن الهجريين، العصر المملوكي، منشورات اتحاد الكتاب العرب، دمشق، سلسلة الدراسات (10)، 2012م، ص28.
[v] محمد أبو الفتوح العفيفي، النص وأدوات تماسكه في قصيدة "شنق زهران" لصلاح عبد الصبور، ضمن مجلة بحوث التربية النوعية، جامعة المنصورة، عدد 28، يناير، 2013، ص417.
This module is designed to enable students to understand concepts of dynamic systems that include electrical, mechanical, and hydraulic components. In addition, it introduces automatic control description, modeling, different control design techniques, analyzing the performance of control systems either in open loop or closed loop, transient-response analysis and steady state error analysis, basic control actions, and Lead and Lag compensators. The frequency response methods using polar plot, bode diagram and Nichol chart, the root locus methods, State space analysis of multivariable control systems, and feedback controllers are also presented.
|
This module aims are: • To help students critically understand the complex set of factors influencing broadcast media institutions;
• To develop a framework for the understanding of the management of broadcast institutions.
• To explore both classic and contemporary theoretical approaches to media management.
This module aims are:
• Cultivate students' awareness of the importance of good vocal performance in Arabic for presentation in broadcast media.
• Give students the opportunity to improve the qualities required for presentation in Arabic in broadcast media through the use of structured exercises.
This module aims:
• To enable students to design, refine and do the preparatory research for the development of an independent, self-directed broadcast project;
• To enable students to produce work which will build on, extend and/or refine issues, practices, concepts and approaches which formed part of their previous learning on their programme of study;
• To promote the development of the skills required for the development of independent project work.
• To allow students to develop project work which will permit a critical reflection on broadcasting and broadcast practice.
Ideas and topics tackled in this unit serve the development of the society through discussing different social problems, community services initiatives, health and well being issues, gender equality, economic growth, reduced inequalities and partnerships. The SDGs are a main theme in this unit, students do extensive research to cover the topic in hand and develop an independent project.
The student uses multiple media as well as computer applications to create examples of media art. Conceptual skills taught enhance student ability to excel in future studies about Visual perception, Internet Interactivity, Animation, Interactive media, & Game design.
This unit covers all concepts relating to 3D form as well as related special issues. The unit will introduce the key skills and professional knowledge needed to creatively develop the built environment and the elements within it. Students will learn how to design real as well as virtual Objects and Products. Analog and digital model-making is an important part of this unit. Students are encouraged to experiment with materials and processes and to question the relationship between form and function. The unit also examines the ethical practice and the role of design in sustaining natural and social environments.
Working in parallel with 2D visualization, this unit aims to develop the student's creative thinking and enhance their imagination capabilities through 3D practice. It also aims to explore the students‘ awareness of the values of both Form and space throughout several workshops and studio practice as well as introductory sessions in 3D digital design
|
Textbook(s) |
||||||||||
|
This course involves diagnosis and treatment plan for restoring teeth with fixed restorations to provide optimum patient care regarding the patient’s condition and demands. It also provides preclinical skills restoring endodontically treated teeth and familiarizes the students with various techniques in restoring endodontically treated teeth with tooth reduction in preparation for the clinical phase followed by taking impression records then, transfer the collected data to the laboratory to fabricate prosthesis fulfilling the proposed plan, followed by trying the restoration and checking it then cementing it . |
||||||||||
|
Grades |
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Fixed Prosthodontics ( 3 Credits) |
||||||||||
|
Course Code:
|
PRS531
|
Prerequisites.
|
||||||||
|
Description |
||||||||||
|
Department: Restorative Dentistry Department, Faculty of Dentistry, MSA Course. The course introduces the student to the more advanced techniques of fixed prosthodontics preparation and construction. Students fulfill their clinical requirements under supervision in the department clinics where the patients have access to treatment completely free of charge |
||||||||||
|
Syllabus |
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
Textbook(s) |
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
Grades |
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Fixed Prosthodontics ( 3 Credits) |
||||||||||
|
Course Code:
|
PRS541n/PRS541
|
Prerequisites.
|
||||||||
|
Description |
||||||||||
|
The course enables the graduating dental student to deal with patients’ complications related to fixed prosthetic appliances. It also introduces the students to the advanced materials, techniques and treatment planning modalities. The course aims at students to recognize implants as a prosthetic option for single and multiple teeth loss, and apply clinical skills acquired in the previous crown and bridge preclinical studies. |
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
Grades |
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
The course spans four semesters.
-The course introduces the student to the clinical application of skills acquired in his previous crown and bridge preclinical training.
-Instruction is focused on early development of diagnosis and treatment planning skills, along with the execution of basic fixed prosthodontics.
-The course also allows interaction between the dental student and the professional dental laboratory technician.
-It also presents more advanced techniques and treatment planning for advanced and complex fixed
prosthodontic needs as well as the principles of crown and bridge in implant dentistry.
|
Syllabus |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Clinical Operative Dentistry 1 course aims to provide the dental students different protocols for proper infection control in addition to the health and occupational hazards of the dental procedure. It also helps them to identify the different types of bases and liners and their application.
Understand the biological influences of dental materials and restorative procedures on health status of dentino-pulpal organ.
This course is concerned with providing the dental students with the art and science of selection of proper restorative material, the different methods of control of pain. It also introduces them to oral environment and moisture control in dentistry, in addition to teeth hypersensitivity and management of deep caries.
This course fulfils SDS3 which is good health and well being.
The aims of the course are to provide the Pharmacologic and clinical knowledge about some commonly occurring clinical problems affecting different body systems and their implications in health promotion. To enable students to understand the safe use of drugs as regards adverse effects, contraindications and drug interactions.
Madness has been a powerful theme in literature, often used to explore the limits of human reason, emotion, and identity. Writers employ it to question social norms, reveal hidden truths, or dramatize inner conflicts that ordinary speech cannot express.
Animal studies is among the budding fields that is attracting a lot of attention over the past two decades. This is partially due to the cultural and conceptual shifts in the figuration of animals from mere objects, serving the humans, to subjects in their own rights. Admittedly, such shifts are triggered by our growing awareness of environmental and animal rights questions in what may be deemed a post-human age.
This module is designed to enable students to understand concepts in computer organization and architecture. Register transfer Statements, and micro operations are studied. Design of arithmetic logic unit, central processing unit, input/output and memory interfaces are illustrated.
LU Code : TR 301
Title : Consecutive Translation
Credit Hours/Points : 3
Level : 3
Prerequisites : TR 100, TR 101, TR 200, TR 201
Learning Outcomes:
Knowledge:
On completion of the course, for consecutive interpretation, students should:
- Indicate and account for the phenomena of oral language communication and transfer and outline the techniques of transferring language and terminology peculiar to different realms of human knowledge.
Skills:
On completion of the course, for consecutive interpretation, students should:
- Develop the intellectual abilities of working memory.
- Produce an oral account in the target language after listening to the source text consecutively.
- Develop the skill of analysing and resolving issues related to translatability problems, linguistic competence, and thus dexterously transfer source language segments from one language to another consecutively.
- Comparing and contrasting structural peculiarities of both English and Arabic languages in various fields.
- Carry out consecutive language transfer in a manageable limited time span under stressful working conditions and professional constrains.
Learning Materials:
Discussion, supervised practice and self-access laboratory interpretation assignments. Passages on various topics will be used as a teaching material.
Assessment:
20% Mid-term Exam
30% Final-term Exam
50% Coursework: 30% for practical, 10% assignments and Portfolio, and 10 % quizzes and a small project
References:
- interpreting: A corpus-based analysis,” Interpreting 7-1, p. 51-76.
- Pöchhacker, F. (in press): “‘Going simul?’ Technology-assisted consecutive interpreting,” in Bao, C. et al. (eds.) Proceedings of the MIIS Anniversary Conference, 9-11 September 2005.
- Pradas Macías, M. (2006): “Probing Quality Criteria in Simultaneous Interpreting: The role of silent pauses in fluency,” Interpreting 8-1, p. 25-43.
- Napier, J. (2003). A sociolinguistic analysis of the occurrence and types of omissions produced by Australian Sign Language–English interpreters. In M. Metzger, V. Dively, S. Collins & R. Shaw (Eds.), From topic boundaries to omission: New research on interpretation (pp. 99–153). Washington, DC: Gallaudet University Press.
- Pöchhacker, F. (2004). Introducing interpreting studies. New York, NY: Routledge. Roy, C. (2000). Interpreting as a discourse process. New York, NY: Oxford University Press. Roy, C. (2005). A discourse-based approach to teaching interpreters. In R. Locke McKee (Ed.), Proceedings of the inaugural conference of the World Association of Sign Language Interpreter, (pp. 91–100). Southampton, UK: Douglas McLean Publishing.
- Russell, D. (2002b). Reconstructing our views: Are we integrating consecutive interpreting into our teaching and practice? In L. Swabey (Ed.), New designs in interpreter education: Proceedings of the 14th National Convention of the Conference of Interpreter Trainers (pp. 5–16). St. Paul, MN: Conference of Interpreter Trainers.
- Russell, D., & Malcolm, K. (2009). Assessing ASL–English interpreters: The Canadian model of national certification. In C. Angelelli & H. Jacobson (Eds.), Testing and assessment in translation and interpreting (pp. 331–376). Amsterdam/Philadelphia: John Benjamins.
- Kalina, Sylvia. 2005. “Quality Assurance for Interpreting Processes“, Meta 50, 2
The teaching of Contrastive Analysis is conceived within the scope of comparing and contrasting Arabic and English in relation to improving Second Language Acquisition and translation through predicting learning difficulties and translation errors that may occur as a result of L1 interference and negative transfer. In this respect, the course participates in providing quality education. Participants are also equipped with approaches and tools of spoken, written and visual text analysis in English and Arabic to assess the impact of the different social contexts on text production and reception. Texts reflect issues of gender, social power as well as health & pandemics.
The unit provides the students with the essential concepts involved in the primary banking credit job, in order to allow the students to be prepared for the intense and competitive banking industry. The unit demonstrates the basic external financing needs of clients, and how to assess the creditworthiness. The unit discusses when and how credit can be provided, monitored and controlled. Also, the unit explains credit risk management and how the bank can hedge against such risks.
- This course is a universal repository for CS100* (and equivalent) courses at MSA with a large number of potential topics that are NOT supposed to be fully covered (neither horizontally nor vertically) during one semester at any faculty.
- Coordinators of CS100* (and equivalent) courses at MSA faculties can use any subset of such topics as long as the course ILOs are fully covered.
- Coordinators of CS100* (and equivalent) courses as well as any other courses at MSA faculties are encouraged to import any topic(s), activity(s), and/or resource(s) they like from this course to their respective courses.
This module investigates and provides an overview of multimedia programming concepts. It aims to two parallel techniques visualization and multimedia techniques. Visualization techniques introduce different methods of programming under GUI (Graphical User Interface) environment. Multimedia techniques introduce skills of animation methods of photometric, and colour images.
Develop relevant programming abilities and demonstrate proficiency with statistical analysis of data. Transform and interpret data using an ethically responsible approach, use appropriate models of analysis, assess the quality of input, derive insight from results, and investigate potential issues. Formulate and use appropriate models of data analysis, languages, and machine learning algorithms, as well as mathematical and statistical models to appropriately formulate and use data analyses
This module is designed to enable students to analyze concepts in the data communication systems including protocols and standards, network configuration and topologies, analog and digital signals, encoding and modulation techniques, interfaces and modems, guided and unguided transmission media, multiplexing, and error detection and correction methods.
The purpose of this module is to provide the students with the fundamental concepts and models of business applications, specifically online transaction processing system (OLTP). Students will apply the concepts and tools studied in the prerequisites. The student will further apply the concepts of program design, problem solving, and fundamental design techniques for event‐driven programs
1- Overall aims of course
• Increase the awareness of the students to the importance of both ethical and biosafety aspects as a rapidly growing field.
• Understand, identify and solve problems in critical, creative and ethical manner
• Recognize the value of self and others in order to be a productive member of a diverse global society.
• Prepare students to embark on related post –graduate studies of interest which would provide better opportunities and advancement in the relevant areas of dental sciences …etc.

This course is designed to provide the dental student with the necessary knowledge to identify the definitions of introductory dental terminology. The course also allows the student to recognize the functions of the human teeth. The student will be able to utilize the correct names and universal code numbers of each permanent and deciduous tooth. The course also provides the student with the general and specific features of permanent teeth.
- This module is designed to provide students with Design of Experiments
- Techniques that are effective for studying the factors that may affect a product or process.
- It also provides students with the capability to analyze experimental
results in order to identify the significant factors and evaluate ways to
improve and optimize the design
This module is the first part of two twin modules teaching the history of economic thought. The aim of this module is to explain and evaluate the evolution of economic thought starting from the Greek times till the mid-nineteenth century and the emergence of Marxist thought.
Although historical, this module contributes in the theoretical economic underpinning of the 2030
Agenda and the role of classical and neoclassical economic theory in this context. Most economic theories – as the 2030 Agenda – are related to
every aspect of sustainability especially those linked to decent work and economic growth (SDG 8), reduced inequality (SDG 10) and peace, justice and strong institutions (SDG 16).
This module is the second part of two twin modules focusing on the history and development of economic thought. The aim of this module is to explain and evaluate the evolution of economic thought starting from the end of the first part module namely the emergence of Marxist thought till the contemporary developments in macroeconomics and microeconomics.
Although
historical, this module contributes in the theoretical economic
underpinning of the 2030
Agenda and the role of classical and neoclassical economic theory in
this context. Most economic theories – as the 2030 Agenda – are related
to
every aspect of sustainability especially those linked to decent work
and economic growth (SDG 8), reduced inequality (SDG 10) and peace,
justice and strong institutions (SDG 16).
This module aims at developing student’s skills with theoretical and practical knowledge on diagnosing the infectious diseases using conventional microbiological, serological and molecular-based diagnostic methods. The module also studies the possible causative agents and the diagnosis of different infectious diseases in the human body system-based manner. The student will learn procedural skills considered in a diagnostic microbiology laboratory including collection, quality control, quality assurance, safety, setup, identification, susceptibility testing and reporting results.
This module is designed enable students to analyze concepts in the binary numbers, number base conversion, complements and codes, definition of Boolean Algebra, Boolean functions, digital logic gates, Integrated circuits, The Karnough Map method (Two–, Three– and Four-variable Maps), POS and SOP simplifications, combinational logic circuits, adders, subtractors, comparators, and code conversions, decoders and encoders, multiplexers and demultiplexers and realization of basic logic gates, and functions generation using combinational logic circuit.
Learning Outcomes: on successful completion of this course a student will be able to:
A. Knowledge:
1- Explain fundamentals of Boolean algebra and building blocks of logic circuits. (K1)
2- Describe common designs of combinational and sequential circuits. (K3)
B. Cognitive Skills:
1- Demonstrate digital logic circuit implementation. (I1)
2- Differentiate between different logic designs. (I2)
C. Professional Skills:
Build logic circuits from common logic gates and components. (P2)
D. General Skills:
Work effectively as a group member. (T3)
Discourse Analysis- frequently known as “language use above the level of the sentence” provides students with the opportunity to study the meaningful production and interpretation of texts and talk. students get introduced to the field of Discourse Analysis in order to unpack texts for generating meaning and bind it with their study of society and culture. They will gain an advanced understanding of the concept of ‘context’ and its relevance in the process of the production of meaning. The course provides students with frameworks and tools to examine and critique texts and instances of language use that is much relevant to socio-economic and socio-cultural issues such as gender, social power and minorities, environment, health and pandemics
Aims
- To understand the principles of DNA technology and its applications on forensic sciences.
- To clarify the terminology and the mail techniques that used in forensic and analysis.
- To be familiar with molecular biological tools and techniques used to perform DNA profiles
- database analysis following DNA forensics applications
Learning Outcomes:
- Understand and appreciate the scope of forensic biology.
- Understand and appreciate the scope, diversity and utility of a variety of DNA typing techniques.
- Perform the primary technique used in Forensic DNA analysis
- identify the equipment and prepare its use to undertake the investigation
Skills learning outcomes:
- consider the health and safety requirements and what precautions need to be taken
- identify the area of the scene, mark it out and protect it to preserve the scene
- handle, package and record evidence
- preserve evidence ensuring its integrity and preventing contamination or degradation
- record relevant information accurately and comprehensively use visual examination and measurement for comparative analysis
- Perform post-PCR Processing
The first course in design theory aims to let the student Understand the design process, with emphasis on the development of a visual language; study of historic, scientific, technological, economic, and cultural factors influencing design in our physical environment.
This module aims to further enhance and complement the students’ knowledge and skills in basic econometrics and to tackle further problems encountered in estimating regression models. The module aims thus to prepare students with the necessary knowledge and skills needed to start their graduate econometrics module. All econometric models built are directly or indirectly linked to several Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) aiming to narrowing the gap economic theory and empirical applications through testing real live data. It is related to reducing poverty, improving health, climate action, sustainable and responsible production and consumption behavior , and enhancement of competitiveness , industries and innovation.
This module is designed to explore the existing and challenging subjects of economic development. The course focuses on the basic concepts of economic development, the development gap, measurement of income distribution and poverty, sources of finance and analyses some of the major development problems and policies.
Many of the United Nations 17 Sustainable Development Goals are discussed in this module especially with respect to the relative success of developing countries in achieving such goals.
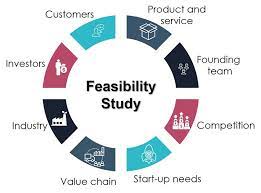
This module aims to provide students with the basic tools for feasibility study preparation including pre-feasibility study, selection of project, financial analysis, and investment appraisal. It provides a brief coverage of the cost-benefit analysis used in evaluating public projects. It allows the students to utilise what they have learned in various courses such as Accounting, Economics, Finance, Marketing and Management, in the preparation of the feasibility study of projects.
This module is designed to provide students with:
1- Introductory topics in the electric circuits that use DC voltages and DC currents.
2- Elements of DC circuits, basic laws and different methods of electric circuit analysis.
3- Analysis, design, and development of
several examples of DC circuits.
This module is designed to enable students to understand, design, and analyze electronic circuits that contain Bipolar Junction Transistors(BJT`s) and Field Effect Transistors (FET`s). ItincludestheoperationandanalysisofBJTandFETamplifiersandstudythe frequency response of both. It provides analysis of multistage amplifiers and current sources. It also provides considerable understanding and confidence in Engineering Electronics and develops the intellectual and practical skills necessary for Electronics Engineering area.
This
module designed to enable students to understand concepts in the electronic amplifier
theory, differential amplifiers, power amplifiers, tuned voltage amplifiers,
feedback amplifiers, sinusoidal oscillators, and operational amplifiers. It
also provides considerable understanding and confidence in Engineering
Electronics and develops the intellectual and practical skills
necessary for Electronics Engineering area.
This module is designed to enable students to focus on the design and analysis of the active circuits, active filters, multiple feedback operational amplifiers, and multiple feedback filters. It also provides considerable understanding and confidence in Engineering Electronics and develops the intellectual and practical skills necessary for Electronics Engineering area.
This course aims to familiarize the student with the clinical phase of treatment with the theoretical topics and correlate with the practical sessions through introducing management pf multiple root canals.
This module is designed to enable students understand the concept of energy conversion, structure and function of power stations, and environmental effects of energy resources. In addition, the principles of magnetic circuits, excitation in single phase transformer, voltage regulation, losses and efficiency, auto-transformation are introduced. It also presents the principles of electromechanical energy conversion, DC generators, DC motors, three phase transformers, polarity, and standard terminal marking, parallel operation, and all-day efficiency. It also addresses the principles of AC machines, Synchronous machine, electro motive force (emf) equivalent circuit, power equation, and distribution of electric power.
|
Words and grammar are the basic building blocks of language. The aim of this course is to introduce contemporary morphological theory and practice. It also introduces the basics of modern syntactic analysis drawing ideas from different syntactic frameworks |
The course is designed to provide the students with basic theoretical concepts of fixed prosthodontics. Biomechanical principles of tooth reduction for full coverage extracoronal restorations are taught regarding all ceramic and porcelain fused to metal restorations. This proceeds in addition to the application of these concepts on anatomic ivorine teeth mounted in models simulating teeth in the oral cavity. Furthermore, the students are trained on the various laboratory steps needed for the laboratory fabrication of Jacket and veneered restorations. This course fulfills the SDS3 which is good health and well being.
This course describes the drugs, chemicals (heavy metals) and plants including their natural products that constitute health hazards, or intended for criminal uses to produce, abortion, loss of mental control, hallucination, heart arrest. Also it includes the study of drug dependents, narcotics, analgesics psycho-energetics, euphoric Mycotoxin as a serious threat to general health and safety of community, contamination of food material with poisonous fungi.
|
This module is designed to provide students with a thorough understanding of the processing by constitution and structure of casting, forming, and joining alloys. Properties and applications of Materials used in Manufacturing .Characteristics of casting, characteristics of forming , characteristics of joining, characteristics of ceramic and Polymer Processing.. |
Production planning is the key of Ready-Made Garments industry. Fashion and design are based on the end consumer retailing on whatever scale it is.
In this course, the main aspect of study is how to conclude a full production plan starting with the basic consumer need (size, design, cost, place of sale, fashion intrusion, etc.) and going back to how to produce such an element in the best cost-effective way taking into consideration many implementations techniques.
Full planning and over-viewing with the market as well as being affected by all the other items of study is the end result of this course.
Many items are affecting our techniques and accordingly the end plan result. Among them are: Quality and its control, merchandise costing, raw material availability and characteristics, location and shipment, purchasing, number of products, timing, production line balancing, pricing, costing, …etc.
This Course is designed to provide students with an understanding of Quantities and Units, Voltage, Current, and , resistance, Ohm's Law, Energy and Power, Series Circuits, Parallel Circuits, Series-Parallel Circuits, Circuit Theorems and Conversions, Branch, Loop, and Node Analyses, Magnetism and Electromagnetism, Introduction to Alternating Current and Voltage, Capacitors, Inductors, Transformers, RC Circuits, RL Circuits, RLC Circuits and Resonance, Passive Filters, Circuit Theorems in AC Analysis, Time Response of Reactive Circuits, and Three-Phase Systems in Power Applications
|
This module is designed to provide students with an understanding of the concepts of thermodynamics and its applications to real thermal processes. The first law of thermodynamics. Working fluids. Reversible and irreversible processes. Second law of thermodynamics. Heat engines and refrigerators, carnot cycle. Modes of heat transfer, steady heat conduction, Newton’s law of cooling. Composite wall and electrical analog, heat flow through cylinders, and a spheres, Forced and natural convection. Heat exchangers
|
This course aims to provide comprehensive knowledge of the basic structure of the human body and its clinical significance. The course provides a strong foundation for future studies. The course deals with human morphology in a systematic approach that starts with the cellular level of organization followed by tissue, organ and system levels. This course fulfills which is good health and well being.
This course introduces a comprehensive study of the regional anatomy of the head and neck with its clinical relevance. This course aims to provide the student with a strong foundation for future clinical and surgical procedures. This course fulfills SDS3 which is good health and well being.
|
This course aims to provide comprehensive knowledge of the basic structure of the human body and its clinical significance. The course provides a strong foundation for future studies. The course deals with human morphology in a systematic approach that starts with the cellular level of organization followed by tissue, organ and system levels. This course fulfills which is good health and well being. |
The Surgery-1 course aims to provide the preclinical student with information about the basic hand skills of suturing and body response to trauma and shock and the proper way of treatment with highlighting on proper intravenous fluids intake principles. Also the course provide the student with information about opthalmology diseases related to dental practice. By the end of this course the student will be able to perform different types of sutures and evaluate trauma patient according to advanced trauma life support system.
This course fulfils SDS3 which is good health and well being
The Surgery-1 course aims to provide the preclinical student with information about the basic hand skills of suturing and body response to trauma and shock and the proper way of treatment with highlighting on proper intravenous fluids intake principles. Also the course provide the student with information about opthalmology diseases related to dental practice. By the end of this course the student will be able to perform different types of sutures and evaluate trauma patient according to advanced trauma life support system.
This course fulfils SDS3 which is good health and well being
The Surgery-2 course aims to provide the preclinical student with information about the head and neck basic structure related to dentistry with different pathological problems and the way of treatment. Also the course provide the student with information about ear, nose and throat diseases related to dental practice. By the end of this course the student will be able to differentiate between different neck swellings and be familiar with patient preparation preoperatively and postoperatively.
This course fulfils SDS3 which is good health and well being
This unit aims to enhance the students’ knowledge and skills needed to conduct a research paper of substantial depth and length under the supervision of a faculty member, whether it is theoretical based on literature review and analysis, or empirical based on econometric, statistical or mathematical analysis.
Topics selected by students for their graduation projects are closely linked to sustainable development goals, especially SDG8 related to decent work and economic growth, as they create models where they try to determine the main catalysts for growth in certain countries or regions. Students also choose topics related to reducing poverty (SDG1) or inequality (SDG10), quality education (SDG4) gender equality (SDG5) and many other SDGs.
FSHN405 course –along with FSHN406- comprise the final Graduation Project in one of the four major fields of the Fashion Design Department in response to a self-initiated design agenda/brief. Students will finally exploit all their expertise and previous experiences acquired throughout their course of study to accomplish their final Fashion Design project.
In this course students will execute one final research project representing their knowledge, skills and cultural awareness gained in the previous years of study. The student will choose one of the four major fields in the Fashion department and will focus all his/her tools to accomplish the desired outcome. Students are expected to hand in a final dissertation reflecting the entire process they went through, the background, the context, the literature review and analysis/ critique.
FSHN405 course will focus on collecting information, literature, analysis in the form of researches, reports, presentations, peer to peer assessment, critiques, and one on one tutorial as well as laying the solid base for the practical visual outcome throughout sketches and technical experimentation. A final dissertation is presented by the end of this course.
This unit aims to enhance the students’ knowledge and skills needed to conduct a research paper of substantial depth and length under the supervision of a faculty member, whether it is theoretical based on literature review and analysis, or empirical based on econometric, statistical or mathematical analysis.
Topics selected by students for their graduation projects are closely linked to sustainable development goals, especially SDG8 related to decent work and economic growth, as they create models where they try to determine the main catalysts for growth in certain countries or regions. Students also choose topics related to reducing poverty (SDG1) or inequality (SDG10), quality education (SDG4) gender equality (SDG5) and many other SDGs.This course explores the origins of Graphic Design starting from the plain Art Poster all the way to the appearance of the sophisticated Graphic Industry apparent and stable in our current life. It’s one of the 3 courses designated to theory & history in the Graphics Major covering the evolution of Graphic Design as well as the principles/concepts that help shape the medium.
Following the topics covered in the course, students’ awareness of the local contemporary culture and surrounding graphic design will be enhanced throughout executing a number of multi-media presentations and reports covering the course topics.
GRPH405 unit–along with GRPH406- comprise the final Graduation Project in one of the four major fields of the Graphics & Media Arts Department in response to a self-initiated design agenda/brief. Students will finally exploit all their expertise and previous experiences acquired throughout their unit of study to accomplish their final Graphics and Media Arts project.
In this unit students will execute one final research project representing their knowledge, skills and cultural awareness gained in the previous years of study that is closely related to the SDGs. The student will choose one of the four major fields in the Graphic and Media Art department and will focus all his/her tools to accomplish the desired outcome. Students are expected to hand in a final dissertation reflecting the entire process they went through, the background, the context, the literature review and analysis/ critique.
GRPH405 unit will focus on collecting information, literature, analysis in the form of researches, reports, presentations, peer to peer assessment, critiques, and one on one tutorial as well as laying the solid base for the practical visual outcome throughout sketches and technical experimentation. A final dissertation is presented by the end of this unit.
- Define types of data, simple model of computer, data storage, data processing, integrated circuits (ICs), and registers.
- Recognize number systems and coding schemas.
- Identify the functions of OS, basics of programming languages, and computer software categories.
- Apply computer skills on mini-projects serving different engineering departments.
- Explain the types of computer networks and data communication.
- Organize the information security, Malicious Software, and solutions.
- Have a view on the concepts and the future of AI & IoT.

THTR455: History of Styles unit is incredibly important to the joy and self-knowledge of nations. It is actually included in the SDGs 4, 8,10, 11 and 16. In this unit student learn to trace back the applications of different SDGs through history and how we can imitate or develop the good practices. For example, they acquire the knowledge of the direct relationship between economy and the power of civilization that is probably reflected in the architecture, furniture and costumes of certain periods. As well as, student can track down ho ancient people tried to solve environmental problems back then like sustainability in the hanging gardens of the new-old Babylon that were in fact the first example of green and blue roof technology employed in urban planning. Studying this unit allows students to be aware of how Inequalities and injustice can affect buildings, costumes and furniture such as in the “Sumptuariae Leges” of ancient Rome were various laws passed to prevent inordinate expense in banquets and dress, such as the use of expensive Tyrian purple dye. In the early years of the Empire, men were forbidden to wear silk. Furthermore, they grasp how wars, conquests and revolutions clearly affected various design styles along historical periods. Why THTR455: History of Styles unit is important for the Global Goals? is associated with Goal 4 – Quality Education, As one of its targets is (4.7) "By 2030, ensure that all learners acquire the knowledge and skills needed to promote sustainable development, including, among others, through education for sustainable development and sustainable lifestyles, human rights, gender equality, promotion of a culture of peace and non-violence, global citizenship and appreciation of cultural diversity and of culture's contribution to sustainable development. Goal 8 – Decent Work and Economic Growth, Since the official wording for Target 8.2 is: "Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification, technological upgrading and innovation, including through a focus on high-value added and labor-intensive sectors. Goal 10 – Promote universal social, economic and political inclusion The target of this goal is "By 2030, empower and promote the social, economic and political inclusion of all, irrespective of age, sex, disability, race, ethnicity, origin, religion or economic or other status" Goal 11 – Sustainable Cities and Communities Target 11.4 is to "Strengthen efforts to protect and safeguard the world's cultural and natural heritage." It has one indicator: Indicator 11.4.1 is the "Total per capita expenditure on the preservation, protection and conservation of all cultural and natural heritage, by the source of funding (public, private), type of heritage (cultural, natural) and level of government (national, regional, and local/municipal)". The full text of Target 11.a is "Support positive economic, social and environmental links between urban, peri-urban and rural areas by strengthening national and regional development planning" Goal 16 – Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions The full text of Target 16.b: "Promote and enforce non-discriminatory laws and policies for sustainable development."
This module aims at providing the students with basic knowledge of the human immune system and the underlying molecular and cellular mechanisms of immune functions in health and disease conditions such as infectious diseases and tumors, in addition to their consequences for immunization and immunological memory. The module discusses the basis of vaccinology, the science field aiming for the prevention and/or treatment of pathologies of infectious or noninfectious (allergy, cancer, others) origin.
This module discusses international trade related theories and policies and their analysis for international trade contexts and it contributes to how can trade deliver key sustainable Development Goals to include and not to be limited to:-
SDG1: Inclusive trade policies will reduce poverty rate
SDG 2: How can trade subsidies cause distortions in agricultural markets and hence affect food sustainability and security
SDG3: How could WHOs TRIPs agreement ensure access to medicine and vaccines.
SDG5: The role of trade in creating jobs to women and unleashing better and more equitable opportunities.
SDG8: The role of trade can lead to inclusive growth and enhance the nations' income generation sources and capability
SDG 9: Improving the competitiveness and preparedness of industries and innovation through specialization and trading .
Lean Manufacturing is about creating value. The Lean process starts with creating value for the ultimate customer which requires providing the right product at the right time for the specified price. While all manufacturing attempts to do this, what makes Lean Manufacturing distinct is the relentless pursuit and elimination of waste. Students will learn the concepts and tools of Lean which include types of waste, visual management, value stream analysis, flow, Just in Time, pull, and Kaizen.
This course focuses on what makes children’s literature for children. The students will address questions such as, what are the defining features of children’s literature? What makes it for children rather than for adults? How does its intended audience shape its form? How do its form and style—including its illustrations—shape its content?
Macroeconomics is concerned with the understanding of aggregate phenomena such as economic growth, business cycles, unemployment, inflation, and international trade among others. ... These topics are of particular relevance for the development and evaluation of economic policy.
This module aims to provide the student with a comprehensive guide to the revolutionary management support system technologies, and how they can be used for better decision making. The module presents the sue of modelling and simulation in the decision process then provides an in depth survey of the use of current IT technologies in DSS such as data warehousing, data mining, OLAP, knowledge management, artificial intelligence and expert system.
This module is designed to provide students with the fundamental of some non- conventional processes such as Chemical Machining (CM), Electrochemical Machining (ECM), Electric Discharge Machining (EDM), Laser Beam Machining (LBM), Electron Beam Machining (EBM), Ultrasonic Machining (USM), Abrasive Jet Machining (AJM), Hydrodynamic Machining (HDM) and Abrasive Flow Machining (AFM). Focus on the use of new tools, concepts, terminology, function and industrial applications of each process of non - conventional processes.
|
This module is designed to provide students with a thorough understanding of the fundamentals of chip - type machine processes. Cutting tools for machining and materials removal. Mechanics and Dynamics of Metal Cutting. Turning, boring and related machining processes. Drilling and related hole making processes, milling, broaching, sawing, shaping and planning, and abrasive machine processes. Creating processes Card, Operation Step card and Operation Sketch. Perform various machining operations, selection of tools, calculation of feed and speed, and machining time.
|
Course Description
This course explores economic principles as they apply to media industries, with a focus on Egypt and the MENA region while integrating global case studies. Students will examine how economic forces shape media ownership, digital transformation, journalism, advertising, and labour markets. Key topics include media monopolies, platform economics, public goods, pricing strategies, game theory in media competition, and regulatory policies.
Course Objectives
By the end of the course, students will be able to:
Apply economic principles to analyze the media industry.
Compare global and regional media market structures and business models.
Examine pricing strategies, revenue models, and consumer behavior in media.
Analyze the impact of digital transformation on labor markets and media production.
Evaluate media regulations and policies in Egypt, MENA, and globally.
Understand economic decision-making using game theory, behavioral economics, and industrial organization.
Biochemical reactions in health and disease are a perquisite to identify and manage health problems. The principal aim of this course is to provide an understanding of the molecular mechanisms fundamental to the life processes. An understanding of the way in which reactions take place at the cellular level will then provide a background against which the changes due to disease can be viewed. -------------------------------------------------------------------(((((((((((((Assessment Pattern )))))))))))) :: *In Course Tests and Quizzes: 10% *Midterm Exam : 10% *Practical Exam : 20% *Oral Exam: 20% *End of Semester Written Exam:40% #Total 100%
This course enables the student to understand how micro-organisms live and infect human, how
human respond to these infections in order to preserve health. The first part of the course presents
basic microbial structure, function, Microbial Genetics, Principles of chemotherapy and drug resistance,
The different methods of sterilization and disinfection in clinics .The second part presents mammalian
host defences and the molecular basis of immunity.
This course enables the student to understand how micro-organisms live and infect humans, and how
humans respond to these infections in order to preserve health. This course presents basic microbial
structure, function and genetics and principles of chemotherapy and drug resistance.
This unit focuses on English teaching methodology. It acquaints students with terms normally used in this area of study e.g. approach, method and technique. It gives them a brief account of the different approaches highlighting the main similarities and differences between them.
The unit examines the following points:
a) Knowledge and skills an English language teacher needs to possess.
b) Similarities and differences between different teaching contexts
c) Similarities and differences between the different teaching approaches.
d) Principles of English language teaching.
How to teach both listening and speaking.This unit discusses the different approaches to, methods and techniques
of teaching reading, writing, grammar and vocabulary in the EFL classrooms. It
explores the varied techniques of error correction and major differences
between young & adult EFL learners.
This module is designed to enable students to focus on the analysis of the Microwave Systems, Waves on an Ideal Transmission Line, Terminated Transmission Lines: Resistive Load, Terminated Transmission Lines: Smith Chart, Impedance Matching, Single-Stub Matching, Quarter-Wave Transformer, Rectangular Waveguides, Circular Waveguides, and Cavity Resonators.
This module aims to covers the factors necessary for successful management of information systems development or enhancement projects. Both technical and behavioral aspects of project management are applied within the context of an information systems development project. The module strikes a balance between both the mechanics of project management and the human factors involved. Software tools for project tracking and monitoring are utilized through out the module.
The purpose of Modern Drama Course is to give an overview and understanding of modern drama from Ibsen to the present.
This course helps students to consider and evaluate a selection of twentieth century fiction in English. It aims essentially to develop a critical appreciation of most outstanding figures in the field of the twentieth century English novel, in relation to their contexts. The course will also focus on some wider questions about the novel as a means of representing its contemporary social and political history.
This course is to emphasize the usefulness of molecular and genetic tools in the diagnosis of diseases. The course explains the impact of genetic polymorphism in altering the response to therapeutic drugs. The course also highlights the role of personalized medicine in tailoring therapeutic dosage to patients individually.
This course aims at introducing the students to detailed description of the molecular basis of cancer and the mechanisms which lead to the initiation and progression of cancer as a serious disease. To this end, hall marks of cancer and the underlying mechanisms are covered in this course. Additionally, the course aims to link this information to how specific cancer drugs are designed based on the important and key alterations studied throughout the course.
Course Specification:
|
Programme Code(s) |
BSc. Hons. Biotechnology (P11493) |
|||||||
|
Host Faculty |
Faculty of Biotechnology |
|||||||
|
Host Department |
Biotechnology |
|||||||
|
Code |
BT309b |
|||||||
|
Title |
Molecular drug design |
|||||||
|
Leader |
Dr. Amr Ageez |
|||||||
|
Level |
4 |
|
5 |
ü |
6 |
|
7 |
|
|
Credit |
4 |
|||||||
|
Pre-requisites |
GEN304b |
|||||||
Aims
- To increase the awareness of the students to the importance of drug design and gene therapy as a rapidly growing field of biotechnology.
- To understand the different methods used to analyze the huge amount of information that is being gathered about human gene sequences and genetic diseases.
- To emphasize upon the integration of basic and applied for creation of strategies for drug design.
Learning Outcomes:
The course outcomes for what students should know include:
- What are the modern methods of the drug design;
- How databases is used to model a pathways, cells, and diseases;
- Mining methods to get the information about pathway or a disease by using databases;
- Application of using modelling in drug design;
- Different strategies of using RNA molecules in gene therapy;
- The advantages, limitations, and dangers of using RNA in gene therapy;
- Different strategies in the design of antiviral drugs, HIV will be used as model for testing these strategies;
This module aims to examine the structure of the banking system, the financial system and the components and functions of money. It also aims to assess methods of determination of interest rates and exchange rates. It also analyses the role of central banks, the process of multiple deposit creation and evaluates the theoretical and empirical aspects of the role of monetary policy in macroeconomic stabilization and economic growth.
This module is linked to the sustainable development goals, especially SDG8 related to decent work and economic growth, as the module teaches students how policy makers can use fiscal and monetary policies in enhancing economic growth.
 On behalf of MSA Family, We'd like to express our pleasure of having you working with us. You were selected to join our professional working family due to the attributes that you demonstrated that appear to match the qualities we look for in a new professional and effective family member.
On behalf of MSA Family, We'd like to express our pleasure of having you working with us. You were selected to join our professional working family due to the attributes that you demonstrated that appear to match the qualities we look for in a new professional and effective family member.
We are looking forward to seeing you grow and develop into an outstanding member that exhibits a high level of care, concern, and compassion for others. We hope that you will find your work to be important, rewarding, challenging, and meaningful.
MSA Family expects your best each day. The Key to your success will be being dependable, individually accountable, responsible, showing openness, following-through, demonstrating high level of attentiveness, exhibiting adequate supervision, effective documentation, Leadership, results oriented and following the policies and procedures. While doing these things you will be successful and so will MSA University. Your professional growth is of utmost concern of MSA, because if you are growing our students grow as well.
Please take your time and review our yearly Organizational, Divisional and Operational goals so that you can learn on organizational expectations. Don't hesitate to discuss your performance goals and expectations with your direct supervisors in order to ensure effective contribution and rewarding.
Act as a MEMBER not an employee
To enhance the understanding of the basic functions, requirements, and food sources of nutrients
(carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, vitamins, minerals, and water) and to apply basic nutrition concepts
to food choices. General concepts of weight management are outlined. Vegetarian and
Mediterranean diets are discussed with their health benefits and hazards. Also, the course aims at the identification of factors that affect dental health highlighting the relationship between dental
disease and nutrition.
|
Operative Dentistry Technology ( 3 Credits) |
||||||||||
|
Course Code:
|
RES351
|
Prerequisites.
|
||||||||
|
Description |
||||||||||
|
This course aims to, apply the mechanical and biological principles of cavity preparation for amalgam, resin composite and cast gold. Understand tooth form and occlusion in relation to operative dentistry . |
||||||||||
|
Syllabus |
||||||||||
|
-Instruments and instrumentation
|
||||||||||
|
Textbook(s) |
||||||||||
|
-James B. Summitt, J. William Robbins, Richard S. Schwartz 2001 Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry, A Contemporary Approach, 2nd ed. Quintessence Publishing
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
This course is designed to provide the dental student with current, basic knowledge of the development, structure and function of the tooth and para tooth soft and hard tissues. The mechanisms of organic matrix formation and mineralization of hard dental tissues. The age changes of hard and soft dental and Para dental tissues.
This course fulfils SDG3 which is good health and well being.
This course is designed to provide the dental student with current, basic knowledge of the development, structure and function of the tooth and para tooth soft and hard tissues. The mechanisms of organic matrix formation and mineralization of hard dental tissues. The age changes of hard and soft dental and Para dental tissues.
This course fulfils SDG3 which is good health and well being.

This course is designed to provide the dental student with current, basic knowledge of the oral and Para oral tissues histology and physiology. The course will deal with the physiological events that happen in the oral cavity as; salivation, eruption and shedding and their clinical considerations. Also the course will give the basic knowledge about human embryology with special reference to the oral and Para oral tissues and organs development.
This course fulfils SDG3 which is good health and well being.
|
Oral Medicine, Diagnosis & Radiology-1 ( 3 Credits) |
||||||||||
|
Course Code:
|
OMD411
|
Prerequisites.
|
|
|||||||
|
Description |
||||||||||
|
-The course aims at establishing didactic information, knowledge and skills necessary for effectively diagnosing and non-surgically treating patients suffering from systemic and/or other local diseases affecting the oral and the head and neck regions. Students fulfill their clinical requirements under supervision in the department clinics where the patients have access to treatment completely free of charge |
||||||||||
|
Syllabus |
||||||||||
|
-Principles of oral diagnosis (the diagnostic method, methods of clinical examination, etc..).
|
||||||||||
|
Textbook(s) |
||||||||||
|
Greenberg M.S. and Click, M.,2003,Burkitt’s Oral Medicine, Diagnosis and Treatment, 10th ed. B. C. Decker.
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
Course Objectives
Host DepartmentOral medicine & Periodontology
Course Code: OMD533z
Course TitleOral Medicine 3
This course will provide general identification of structure & functions of the periodontium with classification of periodontal diseases also detailed information about initiating and predisposing factors of the disease. Finally, the goals, objectives & expected results of non-surgical treatment. It will enable students for clinically performing non-surgical periodontal therapy for mild periodontal cases in the clinic
- Aims/Objectives:
Enable the students to be competent in diagnosing an orthodontic malocclusion, formulating a problem list, and a proper customized treatment plan.
- Course Intended Learning Outcomes (CILOs):
Upon completion of this course, students will be able to:
- comprehensively take Hx & examine an orthodontic patient
- Know how to gather the necessary orthodontic records; manually & digitally.
- Analyze orthodontic records including study model assessment and radiographic interpretation both manually & digitally.
- diagnose an orthodontic malocclusion by formulating an orthodontic problem list and a diagnostic summary.
- Perform a digital diagnostic set-up/treatment simulation (VTO).
- identify the treatment protocols in orthodontic management.
- formulate a treatment plan. & do a case presentation
Orthodontics-1 The course aims to prepare the student to differentiate between the normal occlusion and the malocclusion, link between growth and development study and its clinical application. This course fulfils SDS3 which is good health and well being.
This course prepares the students to Recognize the predisposing and etiological factors that require intervention to promote oral health and to plan appropriate oral health programs for the community. It also enables the dental student to provide preventive measures and instruction in oral health with the preventing dental diseases.
This course fulfills SDS3 which is good health and well being
This course enables the students to: Provide comprehensive dental care for the pediatric patients including variety of disciplines,techniques, procedures, and skills in order to produce a healthy oral and dental in these growing children.
It also provides the dental student with experience in proper management, behavior modification and their ability to establish a positive attitude towards dental treatment in their young patients
The aims of the module are to provide deeper knowledge about commonly used drugs affecting different biological systems and their implications in therapy of diseases and health promotion. It also aims to understand the commonly used safe drugs regarding their adverse effects, contraindications and drug interactions, together with the applied aspects of the pharmacological actions of the major drug groups used in medicine in order to enable them to utilize therapeutic agents in a rational and responsible manner in the treatment of patients.
1- To provide the basic knowledge about commonly used groups of drugs affecting different body systems and their implications in therapy of disease and health promotion especially the analgesics, local anesthetics and drugs affecting bleeding.
2- To enable students to understand the safe use of drugs as regards adverse effects, contraindications and drug interactions.
This course provides students with an understanding of western philosophic concepts that formed the foundations of modern civilization. It also addresses major issues that relate to the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) such as establishing justice & peace, reducing inequalities and building strong political institutions. As such, the course complements knowledge acquired by MSA students of English Studies in the fields of culture, enhances their skills in the analysis of socio-cultural phenomena in literature, develops their Problem-solving skills, communication skills, persuasive powers and writing skills. In addition, the course helps students develop sound methods of research and analysis as well as tools to evaluate and criticize different trends of thought.
This module aims at explaining the basic functions of the different organs of the human body and their correlations
to each other’s. It also demonstrates the pathophysiological changes that occurs as a result of cellular injury and
recognize the relation between the cellular and the system changes which occur in some disease processes with their
clinical manifestation.
|
Upon successful completion of this module, the students should be able to know guidelines for prescribing herbal medicinal drugs based on the pharmacological properties of these drugs including therapeutic uses, mechanism of action, dosage, adverse reactions, contraindications & drug interactions. The module also allows students understand pharmaco-therapeutic principles applied to the treatment of different diseases, pharmacovigilance and rational use of drugs. Also the student should understand the basis of complementary and alternative medicine with emphasis on herbal remedies, nutritional supplements, homeopathies, aromatherapy & their effect on maintaining optimum health and prevention of chronic diseases. It includes studying of medicinal plants portfolios concerning phytopharmaceuticals in Egyptian Market. |
This course is to prepare the postgraduate dental students to start their orthodontic clinical training on patients. It will teach them how to:
- comprehensively take History & examine an orthodontic patient
- Gather the necessary orthodontic records; manual & digital.
- Analyze orthodontic records including study model assessment and radiographic interpretation both manually & digitally.
- diagnose an orthodontic malocclusion by formulating an orthodontic problem list and a diagnostic summary
- Perform a digital diagnostic set-up/treatment simulation
- identify the treatment protocols in orthodontic management.
- formulate a treatment plan. & do a case presentation
- Know how to place separators, orthontic bands and brackets
- fabricate removable retainers, functional applances, soldered appliances and bend multilooped arch wires, T loops, bonded and Essix retainers.
|
This module is designed to enable students to practice the development and design processes of a product within a project, starting from the recognition of a need, passing through conceptual design, materials selection, analysis, optimization, evaluation, prototyping and/or modeling simulation. Criteria for product development to be taken into consideration: ergonomics, safety, manufacturability. Packaging, costing, marketing, uses, reliability, maintainability, environmental impact, and product life cycle.
|
This module is designed to provide students with the knowledge and understanding of the concepts, principles, techniques, and applications of production planning and control. Forecasting techniques, inventory control, planning and scheduling, capacity planning and location, supply chain management, and the current trends in production and service operation management.
|
This module is designed to enable senior students to review and analyze the basic management functions in production systems (manufacturing and service) and associated managerial problems.Basic types of production systems; Design, operation, and performance measures evaluation of batch and job shop production systems; Assembly - line balancing techniques; Design, operation, and performance measures evaluation of continuous production systems; Design and analysis of cellular manufacturing systems. |
- This module is designed to provide students with an analysis of real world complex project systems including planning phase, scheduling phase and control phase.
- The Planning Phase includes network development, precedence diagramming as well as expansion, condensation and elimination of activities.
- The scheduling phase includes deterministic and probabilistic duration times, forward and backward pass computation, slack time calculation, and critical path identification.
- The control phase includes cost control monitor, resource constrains, and time-cost tradeoff. Organization staffing and evaluating alternatives are also included.
- Real case studies.
This course aims to introduce students to the language
of psychology to broaden their understanding of
human nature, as they develop critical understanding of psychological
thinking and research about human development, personality, cognitive
functioning, and mental health. It will familiarize students with the
different perspectives in psychology and help them understand how psychology is
applied. Students will learn how psychology influences everyday activities and
they will be provided with a broad overview of introductory topics in the
discipline.
This course aims at introducing the student to the bases and principles of public health; different measures of disease burden and health status. Different diseases of international public health significance will be reviewed, with a focus on epidemiologic research and methods used to describe and analyze disease determinants. The course also aims at exposing students to different interventions (prevention and control strategies) that are used to reduce the burden of both communicable and non-communicable diseases
|
|
|
This module is designed to provide students with a good understanding of the theories and concepts of total quality management and systems. The topics covered are the views and philosophies of the quality gurus, the development of the quality field from the inspection level to the modern six sigma and Total Quality Management levels, the pillars of total quality, the six sigma perspective to quality management, the implementation and use of the six sigma tools, and the international quality standards. Case studies will be used to introduce and discuss the various components of the course. |

Overall Aims of the Course
This course aims at introducing the students to research in terms of concepts, processes and applications.
Intended Learning Outcomes
By the end of this course, the students should be able to:
Knowledge and Understanding
- Understand the fundamental structure of research
- Understand steps in the methodical processes that lead to valid and reliable results
Intellectual Skills
- Select and define appropriate research problem and parameters
- Read and select appropriate literature
- Prepare a research proposal
- Interpret data
- Conduct research on a particular subject
Practical Skills
- Collect data on a chosen research topic
- Design a step by step framework for the conduction of research
- Analyze data statistically and non-statistically
General and Transferable Skills
- Apply the concepts and skills gained in this course to increase their awareness of English as a language whilst using it in their future academic studies as well as career
|
This module is designed to provide students with a thorough understanding of the robot technology including definition, classification, applications, components, and specification characteristics, robot selection, robot geometry and workspace. Homogeneous transformation matrix, robot kinematic-modeling, and robot motion planning.
|
This course aims at a clear understanding of important texts in the history of theory and criticism and to make these texts useful to students and readers by focusing on their practical value for understanding historical attitudes toward literature, for clarifying current issues in literary theory, and for use in the classroom. The course also aims to examine how criticism has shaped the discipline studied.
|
Semantics and Pragmatics complement each other in language reception and language production. Semantics is the meaning of language, and Pragmatics is language in use. This course aims at introducing students to semantics and pragmatics in terms of concepts, theories and applications at the word, sentence, and text levels. |
LU Code : TR 400 Summer 2023
Module Title : Simultaneous Translation
Level : 4
Credit hours / Points : 3
Prerequisites : TR 100, TR 101, TR 300, TR301
1 – Overall aims of course
This module aims to have students grasp the fundamental concepts and techniques common to simultaneous interpretation, apply the skills and techniques of simultaneous interpretation and interpret in the simultaneous mode on general and semi-specialized topics. Over a period of 15 weeks, besides theoretical lecturing, students are exposed to hands-on experience of simultaneous and conference interpretation, through simulations on different topics , like for example, UN speeches related to its SDGs.
2 – Intended learning outcomes of course (ILOs)
On completion of this unit you should be able to:
- Demonstrate the following knowledge and understanding:
· Detailed knowledge and systematic understanding of the issues, terms and skills related to simultaneous translation
- Demonstrate the following skills and abilities
Perform accurate simultaneous interpretations under stressful conditions and resolve problems arising from oral translations..
Learning Materials:
-A Dictionary of Modern Written Arabic by Hans Wehr (Arabic –English) Edited by J. Milton Cowan.
-A Dictionary of Diplomacy & International Affairs ( English-French-Arabic) by Samouhi fawq El'Adah. Published by Librairie du Liban.
-A Dictionary of Modern Political Idioms ( English-French-Arabic) by Magdi Wahba & Wagdi Ghali.
-Austermuhl, F. 2001. Electronic Tools for Translators. Manchester: St Jerome.
-Barkhudaruf, L. 1993. "The Problem of th Unit of Translation", in P. Zlateva (ed.) Translation as Social Action. London: Routledge, pp. 39-46.
-Amos, F. 1973. Early Yjeories of Translation. New York: Octagon Books.
-Baker, M. 1992. In Other Words: A Coursebook on Translation. London and New York: Routledge.
-Baker M. (ed.). 2008. Routledge Encyclopedia of Translation Studies (3rd ed.). London: Routledge.
-Basil H. 2001 Teaching and Resarching Translation. Essex: Pearson Education.
-Bassnett S 1980/2002 Translation Studies. London:Routledge.
-Baily M (ed.) 1997 The Proceure of The Security Council (3ed). Oxford: Oxford Press.
-Beaugrande, R. de and W. Dressler. 1981. Introduction to Text Linguistics. London: Longman.
-Bush, P. 1997. "The Translator as Reader and Writer", Donaire 8: 13-18.
-Campbelle, S. 1998. Translation into the Second Language. London: Longman.
-Cartellieri, C. "The Inescapable Dilemma: Quality and/or Quantity in Interpreting." Babel 4, 1983.
-Carter, R. And W. Nash. 1990. Seeing Through Language: A Guide to styles of English Writing. Oxford: Basil Blackwell.
-Gentile, Adolfo, Uldis Ozolins & Mary Vasilakakos. Liaison Interpreting: A Handbook. Melbourne: Melbourne University Press, 1996.
-"Language Interpretation". 2011 Retrieved from www.wikipedia.org/wiki/Language_interpretation on 15/9/2011.
-Lochner, R.K. "Conference Interpretation and the Modern World." Babel 3, 1976.
- Los Angeles Chinese Learning Center. 2011."Memory Training in Interpreting". Retrieved from www.chinese-school.netfirms.com on 15/9/2011.
-Simons S. 2002 Targeting Iraq: Sanctions and Bombing in U.S. Policy. (London: Saqi Books).
- ------- 1996 Gender in Translation: Cultural Identity and the Politics of Translation. (London: Routledge).
-Thomas, J. 1995. Meaning in Interaction: An Introduction to Pragmatics. London: Longman.
-Verschueren J. 1999 Understanding Pragmatics. (London: Arnold)
-Vincent A. (ed.) 1997 Political Theory: Tradition and Diversity. (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press).
ابراهيم السامرائي: معجم و دراسة في العربية المعاصرةز بيروت, مكتبة لبنان, 2000.
-ابن منظور: لسان العربز القاهرة, دار المعارف.
-السعيد بدوي: مستويات اللغة العربية في مصر. القاهرة, دار المعارف, 1973.
-محمد عناني: فن الترجمة. القاهرة, لونجمان, 1993.
--- : مرشد المترجم. القاهرة, لونجمان, 2000
Useful Tools:
Software: Adobe Audition
Laboratory
Assessment Scheme:
- The students will be assessed at the final- and mid-term examinations in simultaneous interpreting from and into English.
- The exams and tasks will comprise speeches on a variety of subjects in different registers. The speeches will be prepared to a standard commonly encountered by professional interpreters and delivered as if by practiced speakers. Speeches will be approximately 10 minutes.
Assessment pattern:
Final: 30%
Midterm: 20%
Coursework: 50%
-Tasks 50% (two Tasks; about 6-8 minutes each; one from English into Arabic before the mid and one from Arabic into English before the final; 25 marks each)
Learning Unit Contact Hours Per-Week:
Lecture: 1.5 hours
Extra Tutorial: 3 hours
Total Contact hours per semester: 21 hours
Total Other study hours per semester: 42 hours
Total Study Hours per semester: 63 hours
Module Leader: Dr Safa’a Ahmed
This module is designed to provide students with the necessary knowledge about Direct sequence Code division multiple access (DS-CDMA), Multi carrier techniques: Orthogonal Frequency division multiple access (OFDM) and Multicarrier CDMA (MC-CDMA), Miscellaneous Current and New Technologies: Wide band CDMA(W-CDMA), Ultra Wideband (UWB) communications, Wireless Fidelity (Wi-Fi), and Radio Frequency Identification (RFID).
|
This module is designed to provide students with a thorough understanding of the basic components of stress analysis necessary for analyzing mechanical elements. These include tension, bending, shear, torsion, and combined stresses. Determination of principal stress in structures. It is necessary to develop mathematical relationships in a rational and logical manner, and clearly indicate the conditions that applied safely to the analysis and design of actual engineering structures and machine components.
|
- This course is a universal repository for all courses at MSA with a large number of potential TEL tools.
- Coordinators of all courses at MSA faculties are encouraged to import any resource(s) they like from this course to their respective courses.
This course is considered a test/ practice forum, where you can experience adding/ removing/ editing activities, enrolling users, switching roles, building course blocks and changing structure of the course. you don't need to worry about adding or removing any activity within this course, since it's already created as a practice forum.. do whatever intelligent mistakes you can, to ensure that you are able to create your course properly in the near future. Kindly note that this course will stay open for a while so you can get back to it trying new options and activities free from any worries.
Build simple LANs, perform basic configurations for routers and switches, and implement IPv4 and IPv6 addressing schemes. Configure routers, switches, and end devices to provide access to local and remote network resources and to enable end-to-end connectivity between remote devices.
The course introduces the beginning of the English novel as a literary form throughout the works of some prominent novelists who belong to the eighteenth century. It also casts the light on the major features of the English novel during that age, discussing the various perspectives of the cultural life in England. Moreover, it paves the way for the students to become able to recognize many literary terms and concepts in producing critical analysis of texts, besides using all available internet and software resources available.
This module is designed to provide students with the
principles of tool design. The study includes the design of Jigs and Fixtures, Die
design, single point tool design, and multiple points’ tool design.
The aims of the course are to
Provide the pharmacologic and clinical knowledge about some commonly occurring toxicological problems affecting different body systems and their implications in health promotion.
Enable students to understand the methods of diagnosis and management of common toxicological cases, injuries and emergency medical problems.
The aims of the course are to develop greater understanding about the recent vaccination methods against infectious diseases, as well as to highlight their importance in saving life. The course also interprets why effective vaccines are not yet available for some serious infectious diseases. Besides, the course aims to gain deep information about the current and in progress immunotherapeutic strategies for treating cancer and immunological disorders.
This course casts light on the major literary features of some Victorian novels. It enables students to recognize and analyze the novels of some prominent writers, realizing the style of each writer and the social, political and cultural trends of that era.
|
This module is designed to provide students with an understanding of the scope of methods engineering and time study .Graphic tools for methods analysis .Operation analysis. Worker and machine relationships. Motion study. Micro motion analysis. Human factors considerations. Job analysis and evaluation .Time study requirements and equipment .Performance rating and allowances. Standard time calculation. Predetermined time systems. Work sampling studies. Productivity, wages and incentives. Computer aided time study.
|






